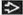Hepatic AD Polycystic Kidney Disease
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Part of fibropolycystic liver (and renal) disease spectrum
Imaging
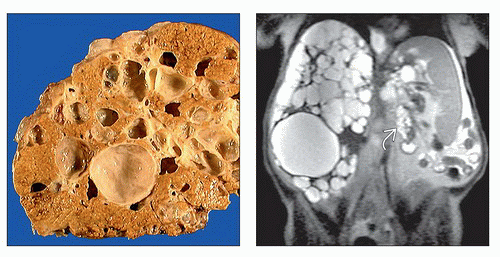
Extent of hepatic involvement ranges from scattered cysts to diffuse replacement of liver
± cysts in kidneys and other organs
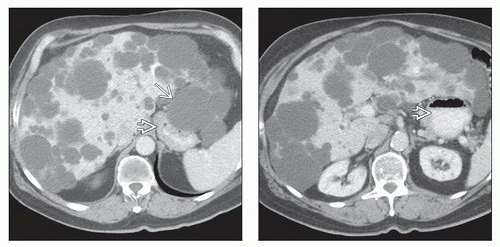
Cyst contents often greater than water density due to hemorrhage (infection less common)
Calcification in cyst wall often seen (due to old hemorrhage)
Cysts have very low signal intensity on T1WI
Higher signal with recent hemorrhage
Homogeneous high signal intensity on T2WI
Intracystic hemorrhage: Lower signal intensity in T2WI
Top Differential Diagnoses
Hepatic (bile duct) cysts
Biliary hamartoma
Caroli disease
Cystic metastases
Clinical Issues
Dull abdominal pain, abdominal distention, dyspnea, cachexia, early satiety
Often causes massive hepatomegaly, compression of stomach
Liver volume often 5-10x higher than normal
Liver progressively enlarges as it is replaced by cysts
Treatment: Surgical marsupialization &/or resection of dominant cysts
Orthotopic liver transplantation has excellent long-term results
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease (ADPLD) or adult PLD
Definitions
Uncommon inherited disorder
Part of fibropolycystic liver disease spectrum
Constitutes group of related lesions of liver and biliary tract caused by abnormal development of embryological ductal plate
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
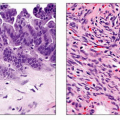
Multiple (> 20) cysts of varying size
Location
Extent of hepatic involvement ranges from limited sporadic areas of cystic disease to diffuse involvement of all lobes of liver
± cysts in kidneys and other organs
Size
Range from < 1 mm to > 12 cm
Key concepts
Numerous large or small cysts coexist with fibrosis
Round or oval shape
Smooth thin wall (if uncomplicated)
Absence of internal structures (if uncomplicated)
CT Findings
NECT
Multiple to innumerable, homogeneous, and hypoattenuating cystic lesions
Cyst contents > water density due to hemorrhage (infection less common)
Calcification in cyst wall often seen (due to old hemorrhage)
CECT
No wall or content enhancement
Cysts complicated by infection or hemorrhage may have septations &/or internal debris
May also have enhancement of walls
Cysts may contain fluid levels
MR Findings
T1WI
Uncomplicated cysts have very low signal intensity
Higher signal in cysts with recent hemorrhage
T2WI
Homogeneous high signal intensity
Intracystic hemorrhage: Lower signal intensity
T1WI C+
Nonenhancing after administration of gadolinium contrast material
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree