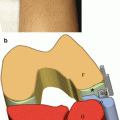
Fig. 4.1
US-guided treatment of hamstring tendinopathy on a long-axis scan. (a) Probe and patient position to perform long-axis US-guided treatment of hamstring tendinopathy. (b) Anatomical scheme and (c) US scan of hamstring tendinopathy treatment. H hamstring muscle, asterisk tendon slip, IT ischiatic tuberosity, arrow needle tip
Rectus femoris enthesopathy: the patient lies in supine position with the lower limb in neutral position. The proximal tendinous insertion is assessed by means of both transverse and longitudinal scans, and the needle is inserted with an in-plane medial-to-lateral or caudo-cranial approach. The procedure is shown in Fig. 4.2 .
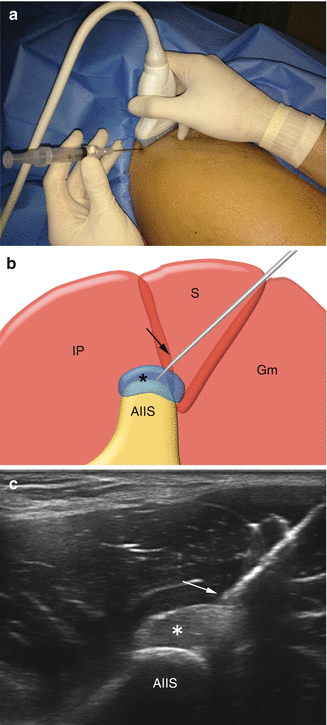
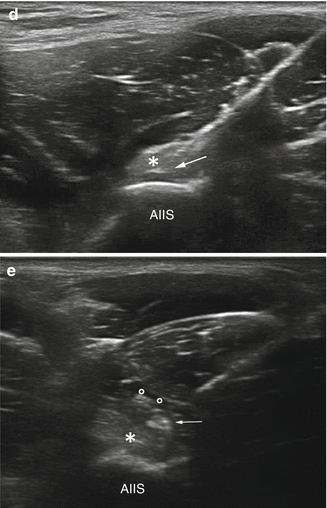


Fig. 4.2




US-guided treatment of rectus femoris tendinopathy on a short-axis scan. (a) Probe and patient position to perform short-axis US-guided treatment of rectus femoris tendinopathy. (b) Anatomical scheme and (c) US scan of rectus femoris tendinopathy treatment. IP iliopsoas muscle, S sartorius muscle, Gm gluteus maximus muscle, asterisk tendon slip, AIIS anterior inferior iliac spine, arrow needle tip. (d) Peritendinous anesthetic (circles) injection. (e) Dry-needling procedure
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree