6 Hormonal and Metabolic Bone Diseases
Osteoporosis
Definition
 Tendency to fracture due to loss of or generalized decrease in bone mass, structure, and function
Tendency to fracture due to loss of or generalized decrease in bone mass, structure, and function
Pathology
 Thinned and rarefied spongiosa
Thinned and rarefied spongiosa
 Widened haversian canals
Widened haversian canals
 Decreased density of the cortex due to imbalance of osseous formation and resorption
Decreased density of the cortex due to imbalance of osseous formation and resorption
Generalized Osteoporosis
Pathology
Categories/Classification
 Primary (idiopathic) osteoporosis:
Primary (idiopathic) osteoporosis:
– Postmenopausal osteoporosis
– Senile osteoporosis
– Juvenile idiopathic osteoporosis
– Presenile idiopathic osteoporosis
 Secondary osteoporosis:
Secondary osteoporosis:
– Endocrine osteoporosis
– Neoplastic osteoporosis
– Gastrointestinal osteoporosis
– Osteoporosis in rheumatoid diseases
– Medication-induced osteoporosis
– Disuse (immobilization) osteoporosis
Clinical Findings
 Pain only after microfractures or macrofractures, usually after inappropriate trauma
Pain only after microfractures or macrofractures, usually after inappropriate trauma
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (Not suited to quantifying the osteoporosis!) (Fig 6.1)
(Not suited to quantifying the osteoporosis!) (Fig 6.1)
Recommended views
 Standard projections
Standard projections
Findings
 Rarefied spongiosa
Rarefied spongiosa
 Thinned cortex
Thinned cortex
 Accentuated appearance of muscular and ligamentous insertions
Accentuated appearance of muscular and ligamentous insertions
 Possibly fractures
Possibly fractures

Indications
 Only supplementary, to work up comminuted fractures
Only supplementary, to work up comminuted fractures

Indications
 Only supplementary in suspected occult fractures
Only supplementary in suspected occult fractures
Goals of Imaging
 Determination of pathological bone density, diffuse/regional
Determination of pathological bone density, diffuse/regional
 Visualization of soft-tissue changes
Visualization of soft-tissue changes
 Visualization of joint-space and cartilage changes
Visualization of joint-space and cartilage changes
 Detection of pathological fractures
Detection of pathological fractures
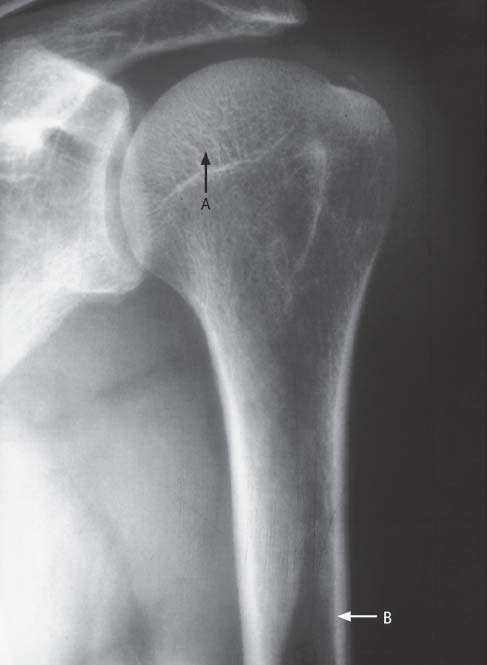
Fig. 6.1  Osteoporosis, conventional radiograph
Osteoporosis, conventional radiograph
A Accentuated trabecular marking due to rarefied spongiosa
B Thinned cortex
Therapeutic Principles
Conservative
 Reduction of risk factors (lack of exercise, inadequate diet)
Reduction of risk factors (lack of exercise, inadequate diet)
 Medication targeting the underlying cause (hormone substitution, Calcitonin)
Medication targeting the underlying cause (hormone substitution, Calcitonin)
Regional (Local) Osteoporosis
Disuse (Immobilization) Osteoporosis after Trauma
Pathology
 Venous stasis due to lack of muscle pump
Venous stasis due to lack of muscle pump
 Active hyperemia in neural injuries
Active hyperemia in neural injuries
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (→ Method of choice)
(→ Method of choice)
Recommended views
 Standard projections
Standard projections
Findings
 Homogenous, band-like metaphyseal, or patchy decrease in bone density
Homogenous, band-like metaphyseal, or patchy decrease in bone density
Sudeck Syndrome
Definition
 Multifactorial trophic disturbance with involvement of soft tissues and bone
Multifactorial trophic disturbance with involvement of soft tissues and bone
Pathology
 Impaired microcirculation due to dysfunction of sympathetic vasocon-stricting neurons
Impaired microcirculation due to dysfunction of sympathetic vasocon-stricting neurons
Clinical Findings
 Pain and hypersensitivity
Pain and hypersensitivity
 Soft-tissue swelling
Soft-tissue swelling
 Vasomotor instability
Vasomotor instability
 Livid discoloration
Livid discoloration
 Functional impairment
Functional impairment
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (→ Method of choice)
(→ Method of choice)
Recommended views
 Standard projections
Standard projections
Findings
 Stage I (early stage):
Stage I (early stage):
– Possibly soft-tissue swelling
 Stage II (acute stage):
Stage II (acute stage):
– Increased radiolucency
– Washed-out spongiosa structure
– Lamellated cortex
– Definite soft-tissue swelling
 Stage III (healing phase):
Stage III (healing phase):
– Increased radiolucency
– Coarse spongiosa structure
– Moderate soft-tissue swelling
 Stage IV (deficient stage):
Stage IV (deficient stage):
– Moderately increased radiolucency
– Scanty spongiosa structure
– Soft-tissue atrophy
 (→ Supplementary method)
(→ Supplementary method)
Recommended sections
 Axial
Axial
 Paracoronal
Paracoronal
 Parasagittal
Parasagittal
Recommended sequences
 T1-weighted spin-echo (SE)
T1-weighted spin-echo (SE)
 T1-weighted SE after intravenous administration of contrast medium
T1-weighted SE after intravenous administration of contrast medium
 Fast spin (echo) T2-weighted inversion recovery (FST2[IR])
Fast spin (echo) T2-weighted inversion recovery (FST2[IR])
Findings
 Stage I:
Stage I:
– Soft-tissue edema: hypointense on T1-weighted images, hyperintense on T2-weighted images
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


