KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Dilation of renal collecting (pelvicalyceal) system ± ureteral dilation from intrinsic or extrinsic cause
- •
Renal collecting system dilation, pelvicalyceal dilatation, pelvocaliectasis
Imaging
- •
Dilated intercommunicating fluid-filled anechoic channels (renal calyces and pelvis) in kidney
- •
Severity of hydronephrosis depends on degree and duration of obstruction
- •
Presence of internal echoes within dilated collecting system may represent underlying infection/pyonephrosis
- •
Acute hydronephrosis: RI > 0.70 or RI 0.08-0.10 higher than normal contralateral side in unilateral obstruction
- •
Antenatal US: Renal pelvis AP diameter ≥ 4 mm prior to 20-week gestation
- •
Fetal renal pelvis diameter ≥ 7 mm at 20-28 weeks or ≥ 10 mm beyond 28-week gestation requires postnatal follow-up
- •
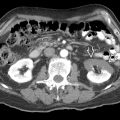
CT has high sensitivity in evaluating site and etiology of obstruction (intrinsic [stone] or extrinsic)
- •
CT may show striated nephrogram &/or urothelial enhancement in superadded infection (pyelonephritis)
- •
CT urogram: Useful in nonstone etiology (urothelial neoplasm, necrosed/sloughed papillae, clot)
- •
MAG 3/DTPA scan: Central photopenic area at vascular phase, tracer accumulation within hydronephrotic collecting system with delayed drainage
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Parapelvic cyst
- ○
Parenchymal cysts that extend into renal pelvis
- ○
- •
Peripelvic cyst
- ○
Ovoid lymphocysts in pelvic hilum, usually multiple
- ○
- •
Extrarenal pelvis
- •
Prominent renal vasculature
- •
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney
Pathology
- •
Chronic obstruction: Loss of renal parenchyma and function
Scanning Tips
- •
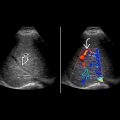
Evaluate with color Doppler to exclude prominent renal vessels in hilum that could mimic hydronephrosis
- •
Look for debris in collecting system, which could indicate pyonephrosis, urologic emergency
- •
Evaluate kidneys after voiding, as mild hydronephrosis may be transient with full bladder
- •
Look for bladder jets, which may help delineate complete from partial obstruction
- •
Look at ureterovesical junction (UVJ) with color Doppler for subtle twinkling artifact, which may indicate distal ureteral or UVJ stone as etiology of hydronephrosis
 in the renal pelvis with mild hydronephrosis
in the renal pelvis with mild hydronephrosis  .
.
 at right ureterovesical junction. Twinkling artifact
at right ureterovesical junction. Twinkling artifact  is seen distal to the stone, which can be useful to identify stones in the urinary system. The ureter proximal to the obstructing stone is moderately dilated
is seen distal to the stone, which can be useful to identify stones in the urinary system. The ureter proximal to the obstructing stone is moderately dilated  . A normal left ureteral jet
. A normal left ureteral jet  is seen on the contralateral side.
is seen on the contralateral side.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree