Hydropneumothorax
Peter J. Noone
Katherine R. Birchard
FINDINGS
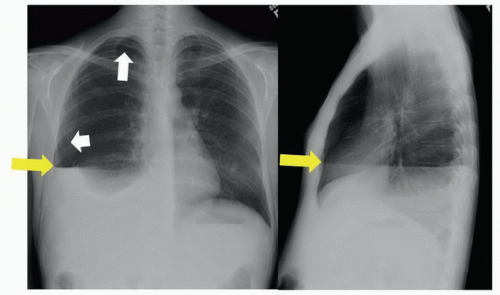
Figure 30A: Upright posteroanterior (PA) chest film shows the visceral pleura (white arrows) of the right lung against a background of black air in the pleural space. An air-fluid level (yellow arrows) in the right pleural space is visible on both PA and lateral films. Note obscuration of right hemidiaphragm.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pneumothorax, pleural effusion, hydropneumothorax, lobar collapse, pneumonia.
DIAGNOSIS
Hydropneumothorax (iatrogenic).
DISCUSSION
Hydropneumothorax occurs when there is both air and fluid in the pleural space. Presenting symptoms include chest pain and shortness of breath, and physical exam reveals decreased breath sounds on the affected side and an audible succession splash. Diagnosis is made with chest X-ray, preferably upright or decubitus. Presence of pleural fluid alone will not result in an air-fluid level; air must also be present in the pleural space to observe an air-fluid level, which should be perfectly horizontal on an upright film. Simple fluid, blood, and pus all have the same density on plain film, so the character of the fluid must be surmised by history or other radiographic findings.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree