and Clarisse Dromain2
(1)
Department of Radiology, San Giovanni Hospital, Roma, Italy
(2)
Department of Radiology, Institut de Cancerologie Gustav Roussy, VilleJuif – Paris, France
Abstract
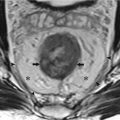
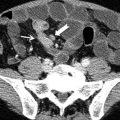
Ileocecal valve is a papillose structure with physiologic sphincter muscle.
Ileocecal Valve Abnormalities
Ileocecal valve is a papillose structure with physiologic sphincter muscle.
It may have variable morphology (from a thin or thick labial structure to rounded morphology).
Lipomatosis is a common abnormality of the ileocecal valve more frequent in women >40 years old. Several abnormalities may affect the ileocecal valve such as lymphoid hyperplasia, inflammatory process (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, parasitic infections), intussusception, and neoplasm.
Neoplasms of the ileocecal valve are represented by lipoma, adenomatous or villous polyp, carcinoid tumor, adenocarcinoma, and lymphoma (often involving the terminal ileum).
Ileus
The term ileus refers to inability of the bowel to push fluid along with intestinal stasis. The term ileus itself does not distinguish between the mechanisms of the stasis (mechanical/nonmechanical causes). For mechanical ileus see Bowel obstruction . Terms nonmechanical ileus, adynamic ileus, and nonobstructive ileus are synonyms referring to intestinal stasis without a mechanical origin.
Possible causes of adynamic ileus in adults are represented by:
Postoperative ileus (usually resolving in 4th postoperative day)
Visceral pain (obstructing ureteral stone, common bile duct stone, twisted ovarian cyst, blunt abdominal or chest trauma)
Intra–abdominal inflammation/infection: peritonitis, appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, salpingitis, abdominal abscess, and ischemic bowel disease
Anticholinergic drugs
Neuromuscular and metabolic disorders: diabetes, hypothyroidism, uremia, hypokalemia, amyloidosis, myotonic dystrophy, CNS trauma, and paraplegia
Systemic disease: Septic and hypovolemic shock
Retroperitoneal disease: Hemorrhage and abscess
Ileus presents with mild dilated small bowel loops without transition zone; after oral iodinated contrast medium administration, a delayed but free passage of contrast material can be detected.
Localized ileus: Isolated distended bowel loop (“sentinel loop”) adjacent to acute inflammatory process (acute pancreatitis, cholecystitis, appendicitis, diverticulitis, ureteral colic).
Inflammatory Polyp
Inflammatory polyps are nonneoplastic polyp of the colon occurring in patients suffering with inflammatory bowel disease.
Infliximab®
Infliximab is the brand name of the most common drug used in biologic therapy of inflammatory bowel disease as well as in many other autoimmune diseases.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree