and Sofia Gourtsoyianni2
(1)
UOC Radiologia BR, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata Verona, Verona, Italy
(2)
Imaging 2, Level 1, Lambeth Wing St Thomas’ Hospital, London, UK
In-Phase and Out-of-Phase Imaging
It is also referred to as chemical shift imaging. Varying the TE of T1-w GRE sequence in-phase (fat and water protons in phase) and out-of-phase (net cancellation of signal: drop of signal intensity in fat-containing areas/lesions) images may be obtained which provide information on parenchymal and lesion fat content (Fig. 1). Opposed-phase images have a shorter TE, normal liver is brighter, and fat-containing areas/lesions demonstrate decrease in signal intensity.
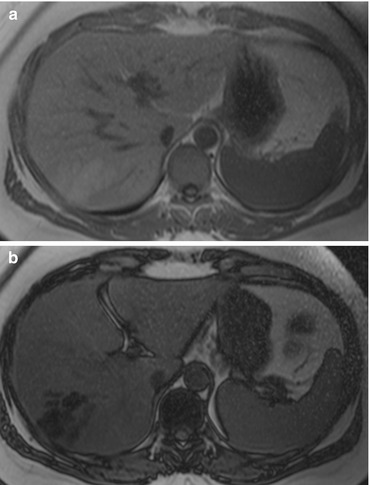

Fig. 1
In phase and out of phase: T1-w GE in-phase (a) and out-of-phase (b) imaging is very useful for characterisation of focal hepatic steatosis by demonstrating signal drop
Inflammatory Pseudotumours (Liver)
Liver inflammatory pseudotumours are rare, benign liver lesions containing fibroblasts, collagen and inflammatory cells that usually present as large infiltrative tumours on imaging with abnormal liver function tests.
Two different patterns have been described: ill-defined, numerous, T2-w hyperintense, active liver lesions and T2-w hypointense lesions, holding a capsule, during nonactive phase.
Biopsy may be required to differentiate from cholangiocarcinoma. They regress spontaneously or after treatment with corticosteroids.
IPMN
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, the most common cystic tumour of the pancreas, is a mucin-producing tumour originating from the epithelium of the main pancreatic duct (main duct type), its side branches (side-branch type) or both (combined type).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree