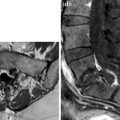
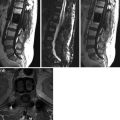
Fig. 1
a–c. Interspinous device X-Stop. a Device. b–c XR lateral and anteroposterior. X-Stop consists of two parallel lateral wings that prevent itself lateral migration connected by a titanium rod or spacer. During implantation, the rod is inserted in transverse way, penetrating the interspinous ligament. It is constrained anteriorly by the lamina, craniocaudally by the spinous processes, and posteriorly by the supraspinous ligament. The rod places the patient in slight flexion, while limiting extension. The flexion obtained by the insertion of the device leads to stretching of yellow ligaments and distracting of nerve foramina
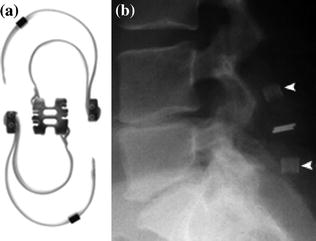
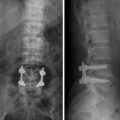
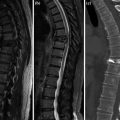
Fig. 2
a–b. Interspinous Wallis. a Device. b XR lateral. Wallis is polyetheretherketone (PEEK), with elastic-like bone characteristics, stabilized with two strips of Dacron. Although it is not truly compressible, properties of material are very close to the elastic modulus of the posterior spine. The two strips of dacron embrace the upper and lower spinous processes, pulled with a special tool. Compared to other interspinous systems also allow to enlarge anterior disk space
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree