Chapter 10 Instrumentation and controls
INTRODUCTION
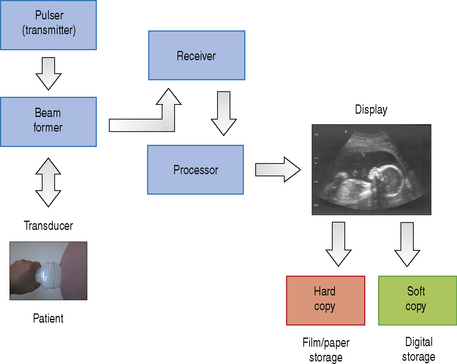
A diagnostic ultrasound machine consists of many components, each of which has a separate operation to perform. This starts with transmitting and receiving ultrasound signals which are then processed to form the images that we see on screen. The internal components that make up a typical ultrasound machine are listed below. Figure 10.1 illustrates the architecture of the components in a block diagram.
COMPONENTS OF A TYPICAL ULTRASOUND MACHINE
The Transducer
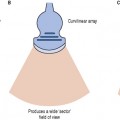
Diagnostic transducers are made from piezoelectric materials (see chapter on Transducers) and are able to convert electrical energy into ultrasound energy and vice versa. As a consequence of this they can act as a transmitter and receiver of ultrasound. They are able to produce beams which can be directed in various ways which are controlled by the ultrasound machine to improve image quality.
The Pulser
The pulser produces the electric voltage that drives the transducer. This driving voltage governs the output power of the ultrasound machine and can be adjusted by the operator through the power or output control. Changes in the applied voltage to the transducer changes the strength and intensity of the ultrasound beam, and affects the overall brightness of the B-mode image. The greater the applied voltage, the stronger the ultrasound pulse and the higher the pulse intensity. Figure 10.2 illustrates the effect that increasing the applied voltage has on the B-mode image. Increasing the applied voltage to the transducer increases the ultrasound pulse intensity, resulting in an increase in the overall brightness of the image.
Processor
The processor can be divided into two individual parts, each having very different tasks to fulfil, and consists of:
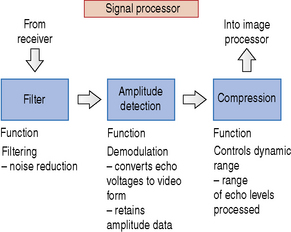
A simple block diagram of the signal processor is illustrated in Figure 10.3. The signal processor picks up the amplified signals from the receiver and carries out operations such as filtering, amplitude detection, and signal compression.
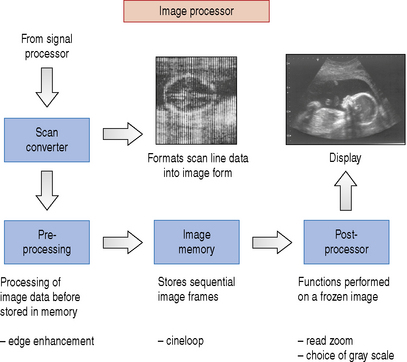
Once the signals have passed through the signal processor they are fed into the image processor. A block diagram of the image processor is illustrated in Figure 10.4. The image processor performs operations such as scan conversion which reformats the scan line data into two-dimensional images, i.e. either linear or sector form. The ability of the scan converter to rapidly process the thousands of scan line data received every second from the transducer enables real-time dynamic ultrasound imaging to be performed.
There is a range of processing performed on the image data prior to and following storage into memory before they are finally sent to the display. Functions such as edge enhancement are known as pre-processing functions because they are performed before being stored.