K
K-space the space that is filled with information and undergoes Fourier transformation to form a magnetic resonance image. By manipulating the K-space, faster sequences can be implemented.
Kaposi’s sarcoma neoplasm characterized by new blood vessel growth producing red, purple or brown lesions, often on the skin, may metastasize to the lymph nodes and viscera. Originally common in Africa but now often seen in immunocompromised individuals, for example, those with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
karyorrhexis disintegration of nuclear chromatin.
Keller’s operation for hallux valgus or rigidus. Removal of the proximal half of the proximal phalanx, plus any bone growths (osteophytes) and bony outgrowths (exostoses) on the metatarsal head. The toe is fixed in the corrected position; after healing a pseudarthrosis results.
keloid an overgrowth of collagenous scar tissue at the site of a skin injury.
Kelvin the unit of thermodynamic temperature.
keratin a fibrous protein found in nails and the outer part of the skin and horns, etc.
keratitis inflammation of the cornea.
keratoacanthoma a benign, rapidly growing, flesh-coloured nodule on the skin with a central plug of keratin. The tumour is most common on the face, back of the hands and the arms.
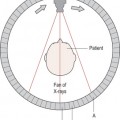
kerma kinetic energy released per unit mass of an absorber, unit joules per kilogram or grays.
ketonaemia ketone bodies in the blood.
ketones organic compounds (e.g. ketosteroids) containing a keto group. ketone bodies include acetone, acetoacetate (acetoacetic acid) and β-hydroxybutyric acid produced normally during fat oxidation. Can be used as fuel but excess production leads to ketoacidosis. This may occur when blood glucose level is high, but unavailable for metabolism, as in poorly controlled diabetes mellitus.
ketonuria ketone bodies in the urine.
ketosteroids steroid hormones that contain a ketone group. The 17-ketosteroids are excreted normally in urine and are present in excess in overactivity of the adrenal glands and the gonads.
keV the energy given to an electron when passing through a potential difference of 1 kilovolt in a vacuum.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree