L
labia (lips) labia majora two large lip-like folds of skin extending from the mons veneris to form the vulva. labia minora two smaller folds lying within the labia majora.
labial (buccal) adjacent to the lips or cheeks.
labioglossolaryngeal relating to the lips, tongue and larynx.
labyrinth the cavities of the internal ear including the cochlea and semicircular canals. bony labyrinth that part which is directly hollowed out of the temporal bone. membranous labyrinth the membrane lining the bony labyrinth.
labyrinthectomy surgical removal of part or the whole of the membra-nous labyrinth of the internal ear. Sometimes carried out for M°ni°re’s disease.
labyrinthitis inflammation of the internal ear.
laceration a wound with torn and ragged edges.
lacrimal, (lachrymal, lacrymal) associated with tears.
lacrimal bone a tiny bone at the inner side of the orbital cavity.
lacrimal duct connects lacrimal gland to upper conjunctival sac.
lacrimal gland situated above the upper, outer canthus of the eye.
lacrimonasal associated with the lacrimal and nasal bones and ducts.
lactacid (lactic) anaerobic system a series of chemical reactions occurring within the cells where a very small amount of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for energy use is produced from glucose, without oxygen. The end product being lactic acid.
lactacid oxygen debt component the amount of oxygen required to remove lactic acid from muscle tissue and blood during the process of recovery from intense exercise.
lactase (β-galactosidase) digestive enzyme present in the small intestine mucosa. It catalyses the hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose.
lactation secretion of milk, the period during which an infant receives nourishment from breast milk.
lacteals the commencing lymphatic ducts in the intestinal villi; they absorb digested fats and convey them to the cisterna chyli.
lactiferous conveying or secreting milk.
lactose deficiency the management depends on severity and may involve the exclusion or restriction of lactose-containing foods.
lacuna a space between cells; usually used in the description of bone.
lamella a thin plate-like scale or partition. A ring of bone round a haversian system. A gelatine-coated disc containing a drug; it is inserted under the eyelid.
lamina a thin plate or layer, usually of bone.
lamina dura a layer of bone forming the outer layer of the socket in which a tooth lies.
lamination layering, soft iron sheets with insulation between each sheet found in a transformer core to reduce eddy currents.
laminectomy removal of vertebral laminae – to expose the spinal cord nerve roots and meninges. Most often performed in the lumbar region, for removal of degenerated intervertebral disc.
LAN (Local Area Network) a number of computers connected together, for example in a hospital.
laparoscopic cholecystectomy removal of the gallbladder using minimally invasive surgical techniques. See also laparoscopy.
laparoscopy (peritoneoscopy) endoscopic examination of the internal organs by the transperitoneal route. A laparoscope is introduced through the abdominal wall after induction of a pneumoperitoneum. A variety of surgical procedures are performed in this way, including biopsy, cyst aspiration, division of adhesions, tubal ligation, assisted conception techniques, appendicectomy and cholecystectomy.
laparotomy incision of the abdominal wall. Usually reserved for exploratory operation.
Larmor equation (ω γBo) the proportional relationship between the precessional angular frequency of a nuclear magnetic moment (ω in Hertz) and the main magnetic field (Bo in Tesla). The gyromagnetic constant (γ) is a proportionality constant and is fixed for the nucleus, for example, 42.6 MHz/Tesla for hydrogen.
Larsen syndrome multiple joint dislocations.
laryngeal associated with the larynx.
laryngeal mask airway with inflatable cuff placed via the mouth into the oropharynx to maintain the airway during general anaesthesia.
laryngeal mirror mirror for inspecting the oral cavity and larynx.
laryngectomy surgical removal of the larynx.
laryngitis inflammation of the larynx.
laryngopharynx the lower portion of the pharynx.
laryngoscope instrument for visualization of the larynx, for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes or to facilitate the insertion of an endotracheal tube into the larynx under direct vision.
laryngoscopy direct or indirect visual examination of the interior of the larynx.
laryngostenosis narrowing of the glottic aperture.
laryngotomy surgical opening in the larynx.
laryngotracheal associated with the larynx and trachea.
larynx the organ of voice situated below and in front of the pharynx and at the upper end of the trachea.
laser (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) a tube in which stimulated emission takes place and the light produced oscillates in a regular pattern to produce a high-energy, coherent, parallel beam of light. Energy is transmitted as heat which can coagulate tissue. Used in the production of modern radiographic images by exposing a film to laser light. Has many therapeutic uses that include: endometrial ablation, detached retina, skin lesions and cancer. Precautions must be taken by those using lasers as eye damage can occur.
laser back pointer mounted in the counterbalance of the gantry of radiotherapy equipment and projects a sheet of light in the direction of the axis of rotation of the gantry and the axis of rotation of the diaphragm system indicating the entry and exit point of the radiation beam.
laser printer characters or images are built up by the image being scanned by a laser and then toner is fused onto the paper to produce the final print.
laser printing film a single-sided emulsion used with imaging plates.
latent image the image produced on a film after exposure but prior to development.
latent period the time between the exposure to a carcinogenic agent and the clinical appearance of disease.
lateral at or belonging to the side; away from the median line.
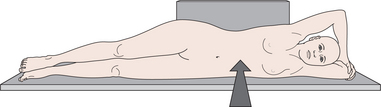
lateral decubitus radiograph the patient lies on their side and the central ray passes from the anterior to the posterior aspect of the body. The projection is named after the side of the body that is uppermost.
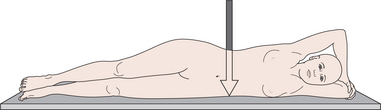
lateral radiograph the patient is either erect or lying with the side of their body nearest the film. The projection is named after the side of the body nearest the film.
lateral resolution in ultrasound, the ability to see small structures that lie along the beam, this is equal to the effective beam width and is best at the focus and reduces the further away from the focus the object is.
latex allergy an allergic reaction to natural latex or one of the components used in production of latex equipment such as medical gloves and catheters. Latex allergy is becoming increasingly common in healthcare workers due to the increased use of gloves following the rise in the incidence of blood-borne viruses.
latissimus dorsi muscle of the back.
latitude the range of useful exposures a film will tolerate. See also useful exposure range.
latitude emulsions a film with a reduced average gradient of 2.2 to enable a large range of densities to be recorded.
laughing gas nitrous oxide (N2O).
lavage irrigation of or washing out a body cavity.
law of conservation of energy energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be changed from one form to another. The amount of energy in a system is therefore constant.
law of conservation of matter matter is neither created nor destroyed, but it may change its chemical form as a result of chemical reaction.
law of conservation of momentum the total linear or rotational momentum in a given system is constant.
laxatives (aperients) drugs used to prevent or treat constipation. Administered orally, or rectally as suppositories or by enema. They may be: bulking agents that retain water and form a large, soft stool; faecal softeners that lubricate or soften the faeces; osmotic laxatives that increase fluid in the bowel lumen; stimulants that increase peristalsis, and combined softeners and stimulants.
lead equivalence a method of comparing protection barriers by calculating the thickness of lead required to have the same absorption to an exposure to radiation.
lead poisoning caused by excessive intake of lead, radiographically, dense transverse lines appear at the shafts of long bones.
lead shielding shielding blocks of lead placed on a tray below the radiotherapy tube to shape the radiation beam so that it accurately covers the treatment area and/or shields organs at risk. Alternative products may be used, usually alloys of bismuth or cadmium. See also MCP block.
lead strip a contouring device formed by placing a lead strip round the patient and the skin markings are transferred to the lead using marker pen, the markings are then copied onto papers giving the patient contour.
leakage radiation unwanted radiation that is emitted from an X-ray tube in directions other than the useful beam, it is reduced by the addition of lead round the X-ray tube.
lecithins a group of phospholipids found in animal tissues, mainly in cell membranes. They are present in surfactant. lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio a test which assesses fetal lung maturity. Below 2.0 is indicative of a higher risk of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
Leeds test objects a number of different test objects produced by the University of Leeds, used for quality control in radiology, to test, for example, film-screen combinations, television systems and CT scanners, etc.
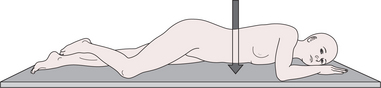
left anterior oblique a radiographic projection with the patient either erect or semi prone at 45° to the film with the left side of the body closest to the film and the right side away from the film.
left colic (splenic) flexure is situated at the junction of the transverse and descending parts of the colon. It lies at a higher level than the right (hepatic) flexure.
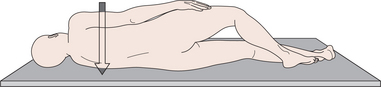
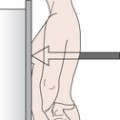
left posterior oblique a radiographic projection with the patient either erect or semi supine at 45° to the film with the left side of the body closest to the film and the right side away from the film (see figure on p. 232).
left ventricular assist device (LVAD)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree