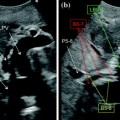
Fig. 11.1
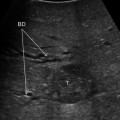
The diameter of the right hepatic vein (RHV) is measured (dotted line) at its root. IVC, inferior vena cava
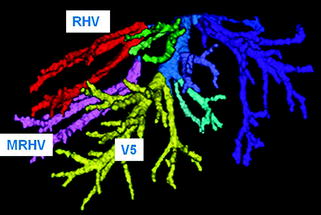
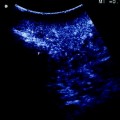
Fig. 11.2
Three-dimensional imaging constructed by a computer software using data of computed tomography. RHV right hepatic vein, MRHV middle right hepatic vein; V5 hepatic vein from the segment 5
The diameter of the main branch that flows back to the right liver and the distance from the branch point to the root of the middle hepatic vein (where it joins the inferior vena cava) are measured in advance, especially when reconstructing the branches of the middle hepatic vein branches in the graft liver (Fig. 11.3a, b). The vein graft that is used for reconstruction is ultimately selected on the basis of these data. We often use thawed cryopreserved allogenic veins, but the great saphenous vein of the donor or recipient can also be used.
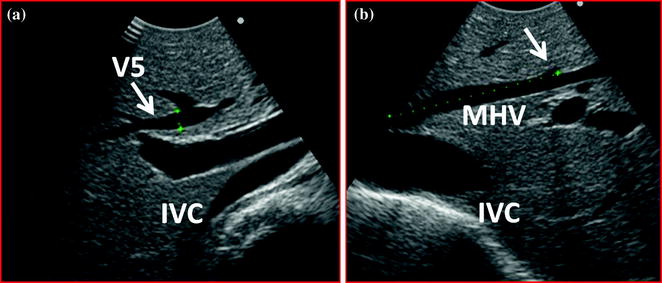

Fig. 11.3
The diameter of the hepatic vein from the segment 5 (V5) is measured at its root (a), and the length between the root of V5 and IVC (the inferior vena cava) is also measured (b; dotted line)
11.3 Hanging Maneuver and Intraoperative Ultrasonography
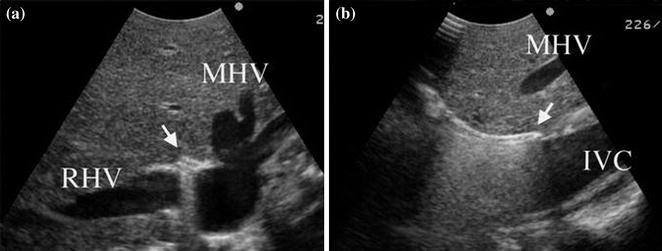
Next, the right liver is mobilized, and, in the initial stage, tape is passed between the posterior aspect of the liver and the anterior surface of the inferior vena cava in preparation for the hanging maneuver [3]. First, on the cranial side, the space between the middle hepatic vein and the root of the right hepatic vein is carefully dissected with sharply curved forceps. If even slight resistance is encountered as this is done, the dissection maneuver is stopped [4]. When examined by ultrasonography with the forceps left in the position, air enters the dissection line, and it is visualized as hyperechoic (Fig. 11.4a, b). It is then possible to check the direction of the dissection and avoid injuring the short hepatic veins. On the caudal side, after dissecting the caudate lobe and inferior vena cava and managing the short hepatic veins that come into view to the extent possible, the forceps is gently inserted in the midline and used to dissect craniad. Here, too, the dissection advanced so that it connects with the line of dissection from the cranial side (visualized as hyperechoic), while examining to see whether there are any short hepatic veins in the path of the forceps (Fig. 11.5a, b).
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

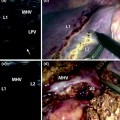
Fig. 11.4
The clamp tip is clearly visualized in the hanging maneuver (a transverse view, b sagittal view) as a strongly hyperechoic structure with a reverberation artifact (arrow). MHV middle hepatic vein, RHV right hepatic vein, IVC inferior vena cava (reproduced from Ref. [4] with permission)

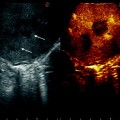
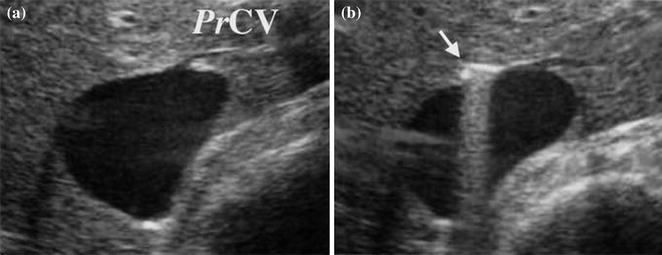
Fig. 11.5
The proper hepatic vein for the caudate lobe (PrCV




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree