Lymphatics
Melissa L. Rosado-de-Christenson, MD, FACR
Gerald F. Abbott, MD
Terminology
Abbreviations
Secondary pulmonary lobule (SPL)
Overview of Pulmonary Lymphatics
Morphology
Tubular structures forming vascular channels
Complex network of vessels and lymphoid tissue aggregates in lung, pleura, hila, and mediastinum
Function
Collection of lymphatic fluid from pleural space, visceral pleura, and pulmonary parenchyma
Conduit of lymphatic fluid towards hila
Anatomy of Pulmonary Lymphatics
General Concepts
Complex network of vascular channels
Reservoir lymphatics; broad, ribbon-like morphology
Conduit lymphatics; tubular morphology
Saculotubular lymphatics; plexiform complex around vessels and bronchi
Bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue
Intrapulmonary lymph nodes
Intrapulmonary peribronchial lymph nodes
General Anatomy
Along airways to level of respiratory bronchioles
Along pulmonary arteries and veins
Within interlobular and connective tissue septa
Within visceral pleural connective tissue
Anatomy of SPL Lymphatics
Peribronchovascular lymphatics
Along lobular pulmonary arteries and proximal lobular airways to level of respiratory bronchioles
Perilobular lymphatics
Along interlobular septa
Visceral pleural lymphatics
Along visceral pleural surface
Imaging of Normal Lymphatics
Normal Intrapulmonary Lymphoid Tissue
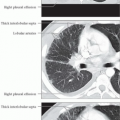
Intrapulmonary lymph node; small, subpleural, or parenchymal, ovoid or elongated, soft tissue nodule
Intrapulmonary peribronchial lymph nodes; small nodular opacities at bronchovascular bifurcations
Lymphatics of SPL
Not normally visible on CT or HRCT
Location of septal and subpleural lymphatics inferred by identification of SPL boundaries: Pulmonary veins and visceral pleural surface respectively
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree