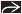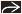Malrotation
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Rotational abnormality of the gut due to arrest of gut rotation and fixation during fetal development
Imaging
Many variations and classifications
Complete nonrotation
Jejunum to right of spine
Ileum to left of spine or in pelvis
Upper GI series with small bowel follow through
Normal barium enema does not exclude malrotation nor volvulus
Classic malrotation
Cecum lies in midline or to left
Fixed in position by bands from undersurface of liver (Ladd bands)
Ladd bands cross duodenum and may obstruct it
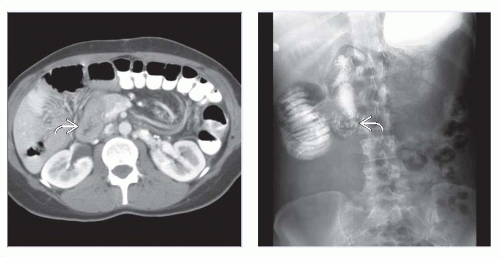
Oral contrast medium ends abruptly or in “corkscrew” pattern within duodenum
CT: Superior mesenteric vein (SMV) ventral to or on left of SMA
Volvulus of midgut indicated by “whirlpool” or “swirl” sign of twisted mesenteric vessels and bowel
CT shows congenital anomalies and complications
Top Differential Diagnoses
Paraduodenal hernia
Clinical Issues
Up to 40% diagnosed by 1 week of age
50% by 1 month
75% by 1 year
25% after 1 year
Some cases of volvulus or obstruction occur in older children or adults
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access 
|