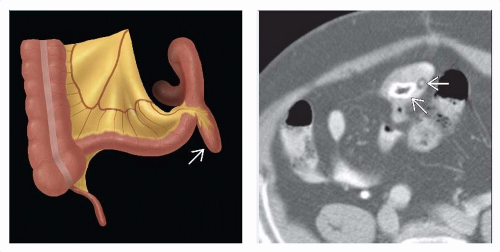
Meckel Diverticulum
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Ileal outpouching due to persistence of omphalomesenteric or vitelline duct
50% contain ectopic gastric mucosa (90% present with GI bleeding in children)
Imaging
Rule of 2s
Seen in ˜ 2% of population
Located within 2 feet of ileocecal valve
Length of 2 inches (on average)
Symptomatic usually before age 2
2 main complications in adults: Diverticulitis (20%) and intestinal obstruction (40%)
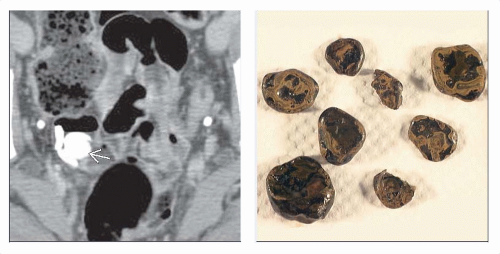
CT: Meckel diverticulitis
Blind-ending pouch containing fluid, air, or particulate matter
Inflamed: Mural thickening of diverticulum and adjacent SB
Shows mural enhancement on CECT
Mesenteric fat infiltration and fluid ± gas ± nodes
± partial or complete small bowel obstruction
± intussusception
Top Differential Diagnoses
Appendicitis
Crohn disease
Mesenteric adenitis and enteritis
Cecal diverticulitis
Clinical Issues
Children: Present with GI bleeding before age 2
Adults: Present with diverticulitis or obstruction
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Meckel diverticulum (MD)
Definitions
Ileal outpouching due to persistence of omphalomesenteric or vitelline duct
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Blind-ended sac or outpouching on antimesenteric border of distal ileum
Size
4-10 cm in length
Morphology
Tubular outpouching of ileum
Other general features
Most common congenital anomaly of GI tract
True diverticulum (contains all layers of bowel wall)
Arises from antimesenteric border of distal ileum
Formed by incomplete obliteration of ileal end of vitelline duct
Usually located within 50-60 cm of ileocecal valve
50% contain ectopic gastric mucosa
± pancreatic, duodenal, and colonic mucosa
90% of cases with bleeding contain gastric mucosa
Fibrous band (obliterated part of vitelline duct may connect apex of diverticulum to umbilicus)
Rule of 2s
Seen in ˜ 2% of population
Located within 2 feet of ileocecal valve
Length of 2 inches (on average)
Symptomatic usually before age 2
2 main complications in adults: Diverticulitis (20%) and intestinal obstruction (40%)
Radiographic Findings
Fluoroscopic-guided enteroclysis
Superior due to maximum luminal distention
Blind-ended sac on antimesenteric border of ileum with either broad base or narrow neck
Broad-based diverticulum
Enteroclysis shows distinctive triangular junctional fold pattern at site of origin
Narrow neck diverticulum
Diagnosis depends on demonstration of blind end of diverticulum and its antimesenteric origin
Appears small initially but fills more completely with increased distention of lumen
Inverted Meckel diverticulum
Seen in 20% of cases
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree