Medial Epicondyle Avulsion
Cassandra M. Sams
CLINICAL HISTORY
10-year-old male with right elbow pain after a fall from a horse.
FINDINGS
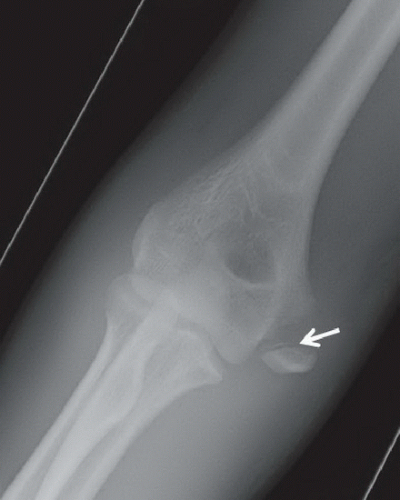
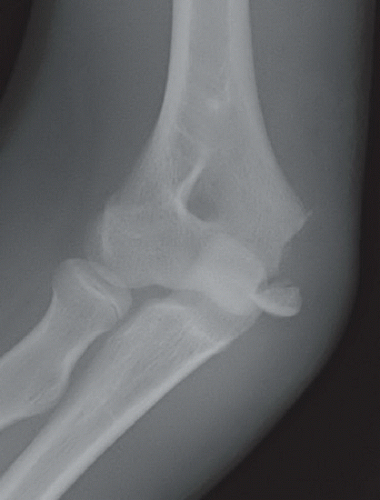
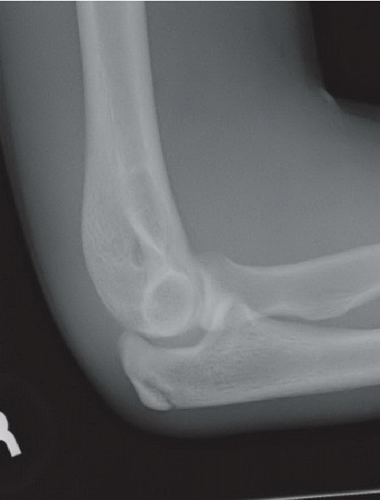
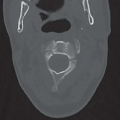
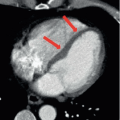
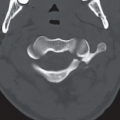
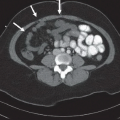
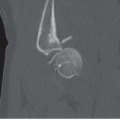
Anteroposterior (Fig. 16A), oblique (Fig. 16B), and lateral (Fig. 16C) radiographs of the elbow demonstrate an ossified body medial and distal to the expected location of the medial epicondyle. An open growth plate (arrow) is noted associated with the ossified body. Marked soft tissue swelling is noted about the right elbow, greater along the medial aspect. No elbow effusion is seen.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Medial epicondyle avulsion, fracture of the medial condyle.
DIAGNOSIS
Medial epicondyle avulsion.
DISCUSSION
The skeletally immature elbow can be a source of confusion owing to the multiple ossification centers, and the varying ages at which they appear. The well-known mnemonic CRITOE (capitellum, radial head, internal/medial epicondyle, trochlea, olecranon, and external/lateral epicondyle) is a helpful memory aid on which to rely. The medial epicondyle is typically seen at around 5 to 7 years of age. Although the exact timing of the appearance of the ossification centers is not important, the order in which they should appear is.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree