Menetrier Disease
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Imaging
Rare condition of unknown cause
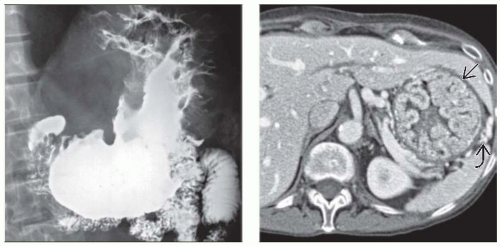
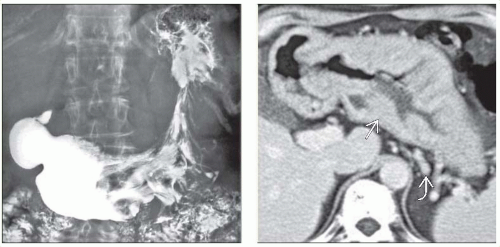
UGI: Grossly thickened, lobulated folds in gastric fundus and body with poor barium coating
CECT: Massive thickening of mucosa and submucosa
Engorged gastric arteries and veins
No extension into perigastric tissues
Histology: Marked foveolar hyperplasia (mucin production) → protein loss → hypoproteinemia
Atrophy of acid-producing cells → hypochlorhydria
Top Differential Diagnoses
Gastritis
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Gastric metastases and lymphoma
Gastric carcinoma
Clinical Issues
Bimodal age distribution
Children (usually boys)
Has been associated with Cytomegalovirus infection
Adults (mean age 55 years)
Prolonged illness in most adults
Complications
Gastric carcinoma may have ↑ prevalence (controversial)
Increased risk of deep venous thrombosis (DVT)
Risk of atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcer, GI bleeding
Medical therapy: Anticholinergic agents, antibiotics, prostaglandins
High-protein diet
May require total gastrectomy
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access 
|