5 Monitor technology
| Aspect Ratio | The ratio of the width of a display screen to the height, e.g. 4 : 3 |
| Bezel | The plastic or metal frame round a display screen |
| Brightness (Luminance) | The amount of light a LCD monitor produces in candela (cd) per square metre (m2), e.g. 250 to 350 cd/m2 |
| Colour Depth | The number of bits used to give the colour of one pixel, and gives the number of different colours that can be displayed at one time, e.g. |
Contrast RatioThe difference in intensity between the black and white on an LCD screen
CursorA flashing marker on the screen which indicates where the next character is to be insertedDot PitchA measure of the sharpness or resolution of a screen
LCDLiquid Crystal Display monitorMonitorA device very similar to a television, but which receives video signals directly from the computerNative ResolutionThe optimum resolution of a LCD monitor. If this is changed the image quality diminishes
Examples of native resolution:
PixelPicture cell. A pixel is the smallest number of dots which can be used by a character on the display screenRefresh RateNumber of times the monitor is scanned by the electron beam per second
ResolutionThe number of ‘dots’ on a monitor screen defines the resolution of a system by describing the number of pixels horizontally and vertically, e.g. 1200 × 1200 gives a resolution of 1200 separate points horizontally and verticallyRGB InputThe colour input on a monitor. The signal from the computer is taken by the monitor as a basic Red, Green and Blue inputScreen SizeCathode ray tubes
Liquid Crystal Display screens
ScrollingThe movement of text or data on the display screen. Scrolling can be upwards, downwards or sidewaysThermionic EmissionThe release of electrons when a substance is heated
VDUVisual display unitViewing AngleThe maximum horizontal and vertical angle that a monitor screen can be viewed at to give a clear image with accurate colours, e.g.
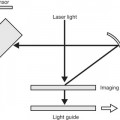
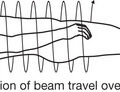
VoxelA three-dimensional pixelInterlacingConsider one still picture on a cathode ray monitor (Figs 5.1, 5.2)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree