6
Musculoskeletal
There will be ten questions on procedures for musculoskeletal imaging in the advanced-level examination for MRI. These will cover the following areas
- Temperomandibular joint
- Upper extremities
- Lower extremities
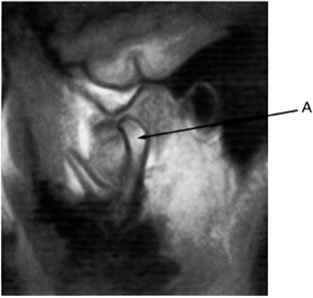
Q100 Image 13 was acquired in the:
| (a) | Axial imaging plane |  |
| (b) | Direct sagittal imaging plane |  |
| (c) | Direct coronal imaging plane |  |
| (d) | Obliqued sagittal imaging plane |  |
Q101 Image 13 is an example of:
| (a) | A T1 weighted image |  |
| (b) | A T2 weighted image |  |
| (c) | A spin (proton) density weighted image |  |
| (d) | None of the above |  |
| (e) | A T2* weighted image |  |
Q102 On image 13, arrow A is pointing to the:
| (a) | Mandibular condyle |  |
| (b) | Temporal bone |  |
| (c) | Disk |  |
| (d) | Masseter muscles |  |
Q103 Image 13 was acquired with:
| (a) | A head coil |  |
| (b) | A body coil |  |
| (c) | No RF coil usage |  |
| (d) | A surface or local coil |  |
Q104 Examination of image 13 reveals:
| (a) | It was acquired with the mouth opened |  |
| (b) | It was acquired with the mouth closed |  |
| (c) | No indication of whether the mouth was opened or closed |  |
| (d) | None of the above |  |
Q105 To evaluate range of motion, temperomandibular joints can be studied with MRI by using a surface coil and acquiring T1 weighted images in the sagittal plane with:
| (a) | The patient’s mouth opened |  |
| (b) | The patient’s mouth closed |  |
| (c) | The patient’s mouth opened and then closed |  |
| (d) | No special instructions to the patient |  |
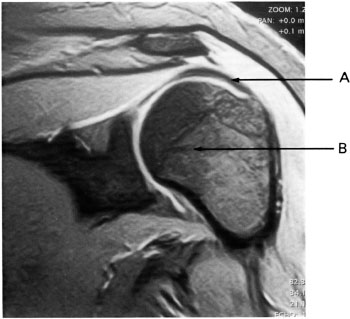
Q106 The coil usually preferred to image the shoulder for the maximization of signal-to-noise ratio is the:
| (a) | Body coil |  |
| (b) | Head coil |  |
| (c) | Surface or local coil |  |
| (d) | Extremity coil |  |
Q107 Image 14 of the shoulder was acquired in the:
| (a) | Oblique sagittal plane |  |
| (b) | Coronal plane |  |
| (c) | Sagittal plane |  |
| (d) | Axial plane |  |
| (e) | Oblique coronal plane |  |
Q108 On image 14, arrow A is pointing to the:
| (a) | Glenoid fossa |  |
| (b) | Rotator cuff |  |
| (c) | Humeral head |  |
| (d) | Deltoid muscle |  |
Q109 Image 14 was acquired with:
| (a) | A spin echo pulse sequence |  |
| (b) | A fast spin echo pulse sequence |  |
| (c) | A gradient echo pulse sequence |  |
| (d) | An inversion recovery pulse sequence |  |
Q110 On image 14, arrow B is pointing to the:
| (a) | Glenoid fossa |  |
| (b) | Rotator cuff |  |
| (c) | Humeral head |  |
| (d) | Deltoid muscle |  |
Q111 To tighten the tendons of the rotator cuff, positioning for shoulder imaging may require:
| (a) | Slight external rotation |  |
| (b) | Slight internal rotation |  |
| (c) | Flexion |  |
| (d) | Extension |  |
| (e) | Neutral position |  |
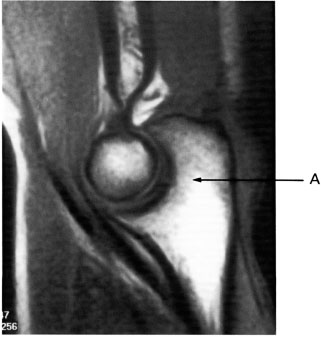
Q112 Image 15 was acquired in the:
| (a) | Axial imaging plane |  |
| (b) | Sagittal imaging plane |  |
| (c) | Coronal imaging plane |  |
| (d) | Off-axis (oblique) imaging plane |  |



