Nerve Sheath Tumors
KEY FACTS
Terminology
Imaging
IMAGING
General Features
Ultrasonographic Findings
 No single feature can reliably differentiate between benign and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
No single feature can reliably differentiate between benign and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
 Clinical indicators are relatively more reliable: Large size (> 5 cm), rapid growth, and change in neurology
Clinical indicators are relatively more reliable: Large size (> 5 cm), rapid growth, and change in neurology
 Irregular margins, inhomogeneity, internal necrosis, and peritumoral inflammation are also more common in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
Irregular margins, inhomogeneity, internal necrosis, and peritumoral inflammation are also more common in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
 NF1 is most important risk factor for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
NF1 is most important risk factor for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
PATHOLOGY
General Features
Gross Pathologic & Surgical Features
 Mesenchymal tumors with cellular differentiation to Schwann cells; myelin-producing neuroglial cells covering peripheral axons
Mesenchymal tumors with cellular differentiation to Schwann cells; myelin-producing neuroglial cells covering peripheral axons
 True capsule composed of epineurium
True capsule composed of epineurium
 Tumors lie eccentric to nerve with nerve fascicles displaced to periphery of tumor mass
Tumors lie eccentric to nerve with nerve fascicles displaced to periphery of tumor mass
 Tend to be more prone to myxoid degeneration, hemorrhage, and calcification
Tend to be more prone to myxoid degeneration, hemorrhage, and calcification ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nerve Sheath Tumors





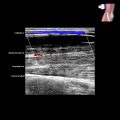
 in continuity with the ulnar nerve with posterior acoustic enhancement
in continuity with the ulnar nerve with posterior acoustic enhancement  . Note the entering and exiting components of the ulnar nerve
. Note the entering and exiting components of the ulnar nerve  .
.
 shows a moderate degree of intralesional hypervascularity. The lesion is arising from the neurovascular bundle and is located alongside the ulnar artery
shows a moderate degree of intralesional hypervascularity. The lesion is arising from the neurovascular bundle and is located alongside the ulnar artery  . Note the moderate posterior acoustic enhancement
. Note the moderate posterior acoustic enhancement  .
.
 from the deep peroneal nerve. The peroneal nerve is thickened
from the deep peroneal nerve. The peroneal nerve is thickened  proximally due to tumor extension along the nerve. Note the ankle joint
proximally due to tumor extension along the nerve. Note the ankle joint  .
.
 with a central myxoid component
with a central myxoid component  and prominent posterior acoustic enhancement arising from the sciatic nerve
and prominent posterior acoustic enhancement arising from the sciatic nerve  . Note the strong posterior acoustic enhancement.
. Note the strong posterior acoustic enhancement.