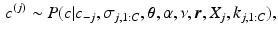and an ordering 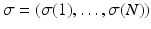 , where
, where 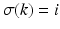 means that event
means that event 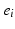 occurs in position k. In practise we only observe a snapshot of the event sequence for each subject, taken at an unknown stage k. If a subject is at stage k in the sequence
occurs in position k. In practise we only observe a snapshot of the event sequence for each subject, taken at an unknown stage k. If a subject is at stage k in the sequence 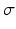 the events
the events 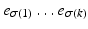 have occurred and events
have occurred and events 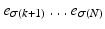 have yet to occur. This adduces a partition of the event set, or partial ranking,
have yet to occur. This adduces a partition of the event set, or partial ranking, 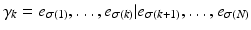 , where the vertical bar indicates that the first set of events precedes the second. The occurence of event
, where the vertical bar indicates that the first set of events precedes the second. The occurence of event 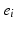 in subject j is informed by biomarker measurement
in subject j is informed by biomarker measurement 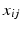 . The generative model of the biomarker data is
. The generative model of the biomarker data is
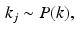
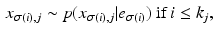
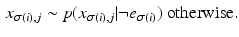
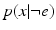 are probability density functions on observing biomarker measurement x given that event e has or has not occurred respectively. P(k) is a prior on the disease stage k.
are probability density functions on observing biomarker measurement x given that event e has or has not occurred respectively. P(k) is a prior on the disease stage k.2.2 The Generalised Mallows Event-Based Model
We formulate the generalised Mallows event-based model by using a generalised Mallows model to parameterise the variance in a central event sequence 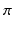 through the spread parameter
through the spread parameter 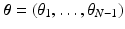 . Each subject then has their own latent ordering
. Each subject then has their own latent ordering 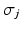 , which is assumed to be a sample from a generalised Mallows model. The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is therefore preceded by
, which is assumed to be a sample from a generalised Mallows model. The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is therefore preceded by
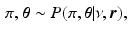
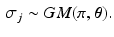
![$$GM(\pi , \varvec{\theta }) = \frac{1}{\psi (\varvec{\theta })} \exp \left[ -d_{\varvec{\theta }} (\pi , \sigma ) \right] $$](/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/A339424_1_En_56_Chapter_IEq15.gif) is a generalised Mallows distribution with
is a generalised Mallows distribution with 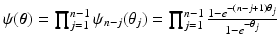 .
. 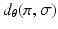 is the generalised Kendalls tau distance [8], which penalises the number of pairwise disagreements between sequences.
is the generalised Kendalls tau distance [8], which penalises the number of pairwise disagreements between sequences. 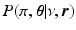 is a conjugate prior over the generalised Mallows distribution parameters of the form
is a conjugate prior over the generalised Mallows distribution parameters of the form ![$$P (\pi , \varvec{\theta } | \nu , \varvec{r}) \propto \exp \left( -\nu \sum _{j} [\theta _{j} r_{j} + \ln \psi _{n-j} ( \theta _{j} ) ] \right) $$](/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/A339424_1_En_56_Chapter_IEq19.gif) [12].
[12].
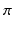 through the spread parameter
through the spread parameter 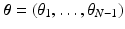 . Each subject then has their own latent ordering
. Each subject then has their own latent ordering 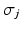 , which is assumed to be a sample from a generalised Mallows model. The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is therefore preceded by
, which is assumed to be a sample from a generalised Mallows model. The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is therefore preceded by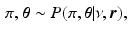
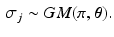
![$$GM(\pi , \varvec{\theta }) = \frac{1}{\psi (\varvec{\theta })} \exp \left[ -d_{\varvec{\theta }} (\pi , \sigma ) \right] $$](/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/A339424_1_En_56_Chapter_IEq15.gif) is a generalised Mallows distribution with
is a generalised Mallows distribution with 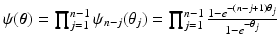 .
. 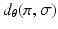 is the generalised Kendalls tau distance [8], which penalises the number of pairwise disagreements between sequences.
is the generalised Kendalls tau distance [8], which penalises the number of pairwise disagreements between sequences. 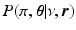 is a conjugate prior over the generalised Mallows distribution parameters of the form
is a conjugate prior over the generalised Mallows distribution parameters of the form ![$$P (\pi , \varvec{\theta } | \nu , \varvec{r}) \propto \exp \left( -\nu \sum _{j} [\theta _{j} r_{j} + \ln \psi _{n-j} ( \theta _{j} ) ] \right) $$](/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/A339424_1_En_56_Chapter_IEq19.gif) [12].
[12].2.3 Dirichlet Process Mixtures of Generalised Mallows Event-Based Models
Dirichlet process mixtures of generalised Mallows models assume that each subject has their own central ordering 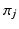 and spread parameters
and spread parameters 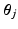 , which are sampled from a discrete distribution G that is drawn from a Dirichlet process [9]. A Dirichlet process mixture is a generative clustering model where the number of clusters is a random variable, meaning that the number of clusters is detected automatically depending on the concentration parameter
, which are sampled from a discrete distribution G that is drawn from a Dirichlet process [9]. A Dirichlet process mixture is a generative clustering model where the number of clusters is a random variable, meaning that the number of clusters is detected automatically depending on the concentration parameter 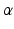 . The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is now preceded by the process
. The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is now preceded by the process
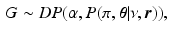
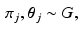
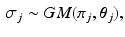 where
where 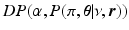 is a Dirichlet process [9]. Each data point
is a Dirichlet process [9]. Each data point 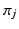 can be characterised by an association with a cluster label
can be characterised by an association with a cluster label 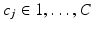 and each cluster c with a set of generalised Mallows parameters
and each cluster c with a set of generalised Mallows parameters 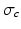 and
and 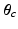 .
.
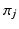 and spread parameters
and spread parameters 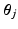 , which are sampled from a discrete distribution G that is drawn from a Dirichlet process [9]. A Dirichlet process mixture is a generative clustering model where the number of clusters is a random variable, meaning that the number of clusters is detected automatically depending on the concentration parameter
, which are sampled from a discrete distribution G that is drawn from a Dirichlet process [9]. A Dirichlet process mixture is a generative clustering model where the number of clusters is a random variable, meaning that the number of clusters is detected automatically depending on the concentration parameter 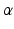 . The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is now preceded by the process
. The generative model of the biomarker data in the event-based model is now preceded by the process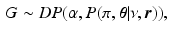
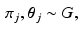
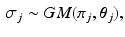
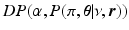 is a Dirichlet process [9]. Each data point
is a Dirichlet process [9]. Each data point 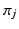 can be characterised by an association with a cluster label
can be characterised by an association with a cluster label 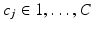 and each cluster c with a set of generalised Mallows parameters
and each cluster c with a set of generalised Mallows parameters 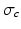 and
and 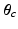 .
.3 Inference
3.1 The Event-Based Model
Inference in the event-based model can be performed by taking Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) samples of 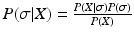 where
where
![$$\begin{aligned} P(X | \sigma ) = \prod _{j=1}^{J} \left[ \sum _{k=0}^{K} P(k) \left( \prod _{i=1}^{k} p(x_{\sigma (i) , j} | e_{\sigma (i)}) \prod _{i=k+1}^{N} p(x_{\sigma (i) , j} | \lnot e_{\sigma (i)} ) \right) \right] \!. \end{aligned}$$](/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/A339424_1_En_56_Chapter_Equ1.gif)
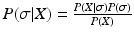 where
where![$$\begin{aligned} P(X | \sigma ) = \prod _{j=1}^{J} \left[ \sum _{k=0}^{K} P(k) \left( \prod _{i=1}^{k} p(x_{\sigma (i) , j} | e_{\sigma (i)}) \prod _{i=k+1}^{N} p(x_{\sigma (i) , j} | \lnot e_{\sigma (i)} ) \right) \right] \!. \end{aligned}$$](/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/A339424_1_En_56_Chapter_Equ1.gif)
(1)
3.2 The Generalised Mallows Event-Based Model
We use Gibbs sampling to infer the parameters of the generalised Mallows event-based model. This consists of two stages. First, generating a set of sample event sequences 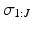 . We sample from an augmented model [10], by alternating between sampling a subject’s ordering
. We sample from an augmented model [10], by alternating between sampling a subject’s ordering 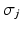 and disease stage
and disease stage 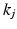 , which are used to deterministically reconstruct their partial ranking
, which are used to deterministically reconstruct their partial ranking 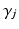 . The Gibbs sampling updates are therefore
. The Gibbs sampling updates are therefore
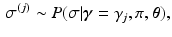
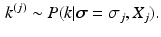 Second, sampling the model parameters given the set of sample orderings
Second, sampling the model parameters given the set of sample orderings 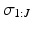 using the updates
using the updates
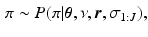
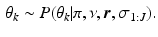
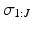 . We sample from an augmented model [10], by alternating between sampling a subject’s ordering
. We sample from an augmented model [10], by alternating between sampling a subject’s ordering 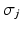 and disease stage
and disease stage 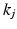 , which are used to deterministically reconstruct their partial ranking
, which are used to deterministically reconstruct their partial ranking 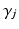 . The Gibbs sampling updates are therefore
. The Gibbs sampling updates are therefore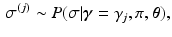
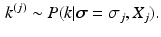
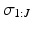 using the updates
using the updates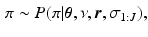
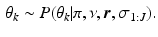
3.3 Dirichlet Process Mixtures of Generalised Mallows Event-Based Models
We formulate another Gibbs sampler to infer the parameters of Dirichlet process mixtures of generalised Mallows event-based models. We generate a set of candidate sample orderings 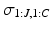 , disease stages
, disease stages 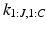 , and partial rankings
, and partial rankings 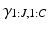 , which are conditioned on the parameters for each cluster via the updates
, which are conditioned on the parameters for each cluster via the updates
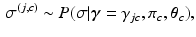
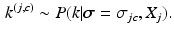 From these samples we sample the cluster assignment
From these samples we sample the cluster assignment 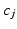 of each subject conditioned on the cluster assignments of the other subjects
of each subject conditioned on the cluster assignments of the other subjects 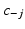 , where
, where 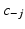 is the set of cluster assignments for all subjects except subject j, the subject’s sample ordering for each cluster
is the set of cluster assignments for all subjects except subject j, the subject’s sample ordering for each cluster 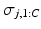 , disease stage
, disease stage 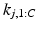 and their biomarker data
and their biomarker data 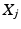 . We then update the generalised Mallows model parameters for each cluster,
. We then update the generalised Mallows model parameters for each cluster, 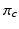 and
and 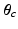 , from the set of subject orderings assigned to each cluster,
, from the set of subject orderings assigned to each cluster, 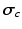 . So we have the updates
. So we have the updates
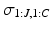 , disease stages
, disease stages 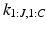 , and partial rankings
, and partial rankings 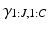 , which are conditioned on the parameters for each cluster via the updates
, which are conditioned on the parameters for each cluster via the updates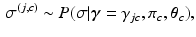
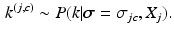
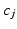 of each subject conditioned on the cluster assignments of the other subjects
of each subject conditioned on the cluster assignments of the other subjects 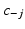 , where
, where 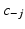 is the set of cluster assignments for all subjects except subject j, the subject’s sample ordering for each cluster
is the set of cluster assignments for all subjects except subject j, the subject’s sample ordering for each cluster 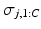 , disease stage
, disease stage 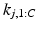 and their biomarker data
and their biomarker data 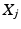 . We then update the generalised Mallows model parameters for each cluster,
. We then update the generalised Mallows model parameters for each cluster, 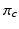 and
and 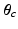 , from the set of subject orderings assigned to each cluster,
, from the set of subject orderings assigned to each cluster, 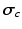 . So we have the updates
. So we have the updates