133 Duodenum lateral to head of pancreas
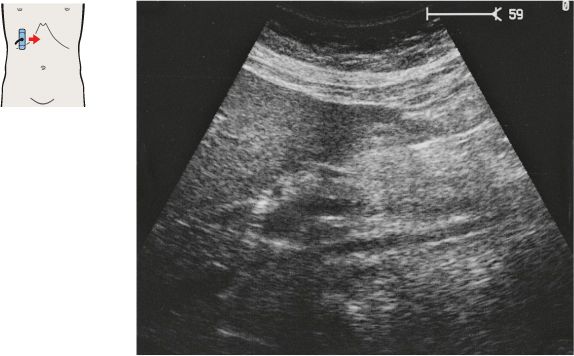
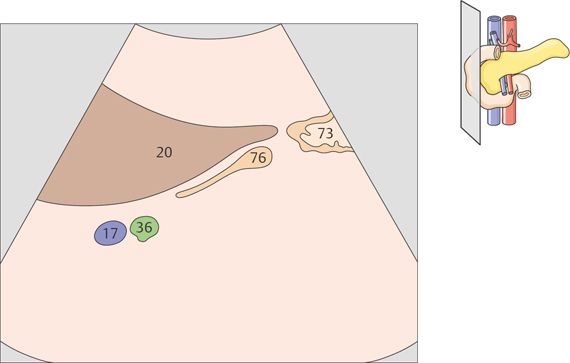
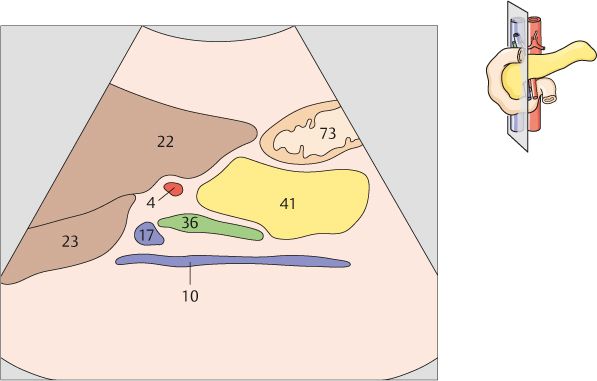
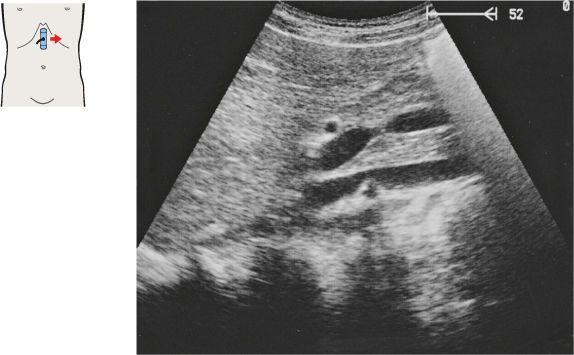
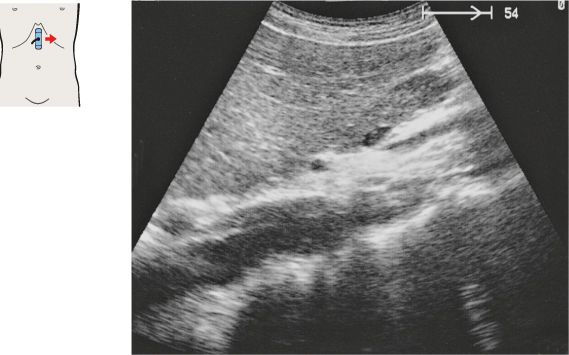
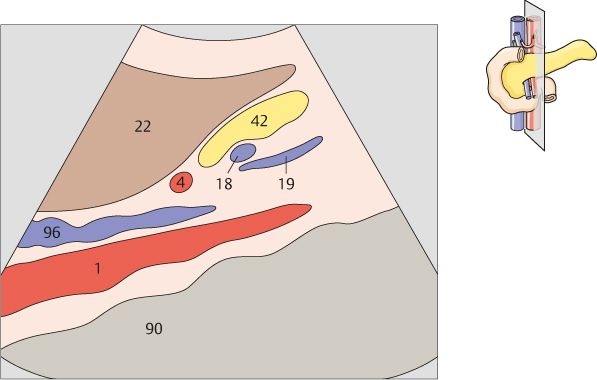
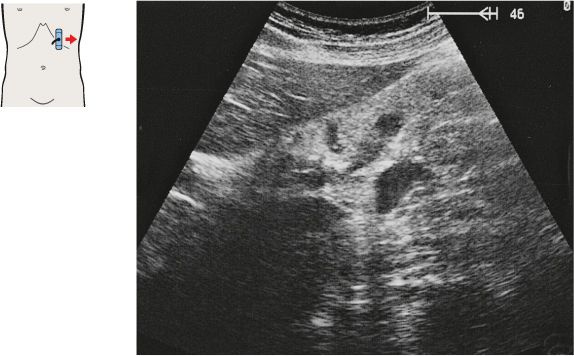
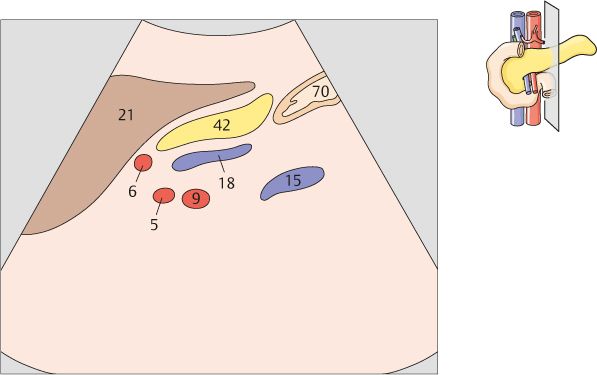
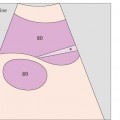
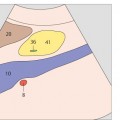
134 Head of pancreas, bile duct
The head of the pancreas lies in the duodenal loop of the duodenum and is bounded laterally by the duodenum.
The bile duct, hepatic artery, and portal vein are located cranial to the head of the pancreas.
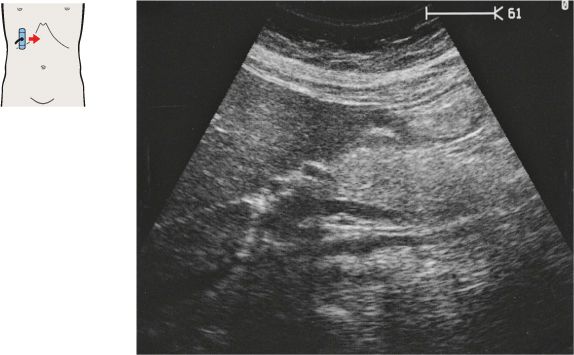
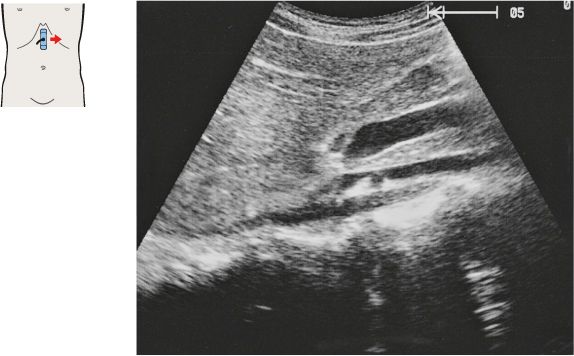
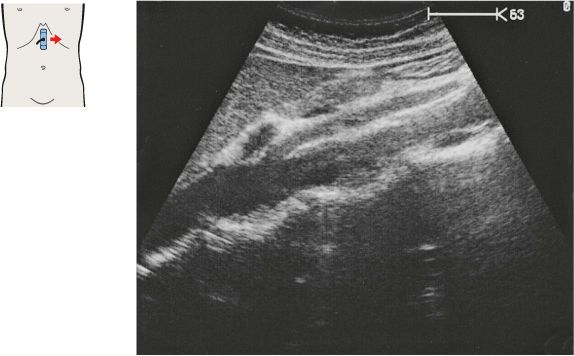
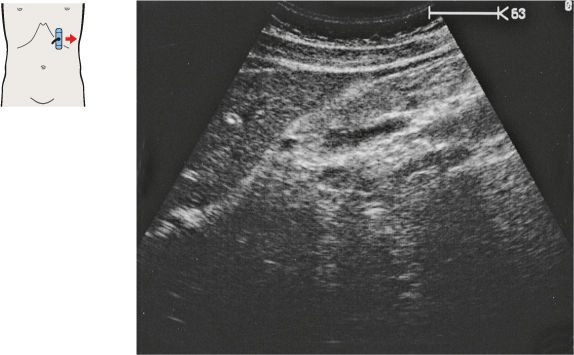
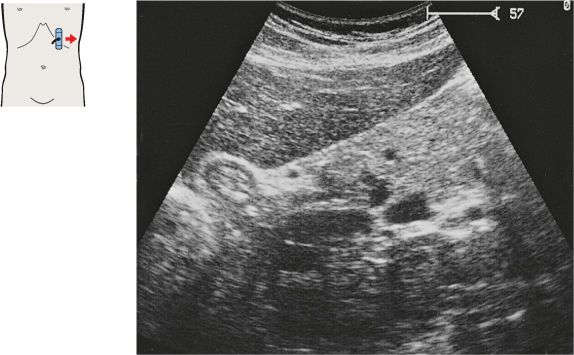
135 Head of pancreas, bile duct
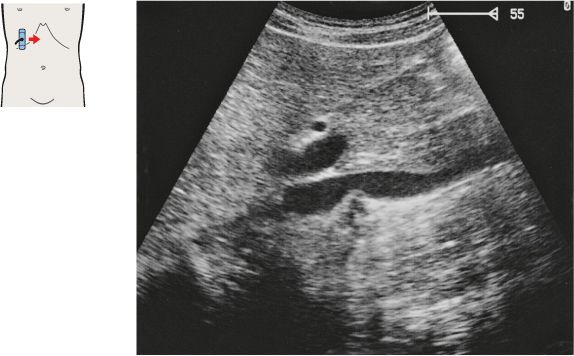
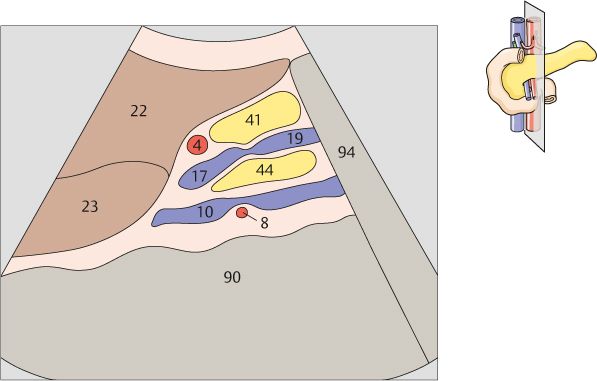
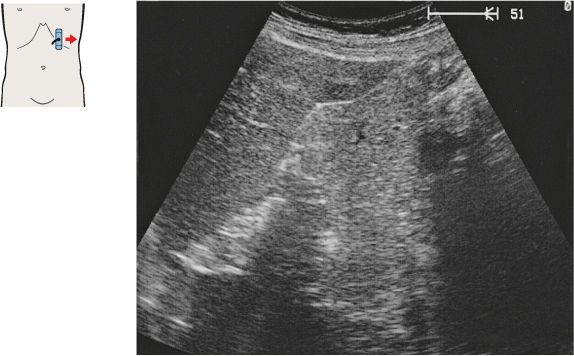
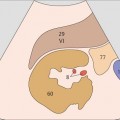
136 Head of pancreas, hilar vessels, vena cava
The bile duct runs posteriorly in the head of the pancreas to the papilla, which usually cannot be visualized with ultrasound.
The head of the pancreas lies against the anterior surface of the vena cava and is bordered cranially by the main trunk of the portal vein.
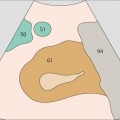
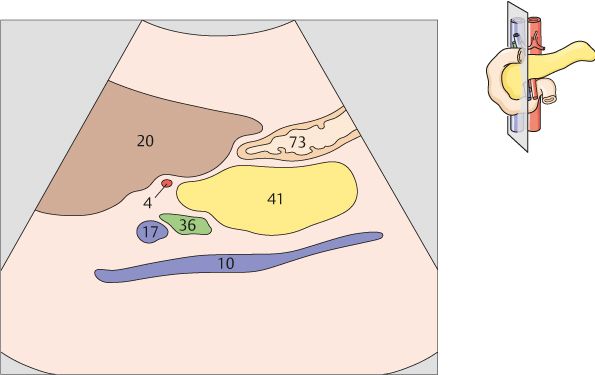
137 Head of pancreas, superior mesenteric vein, uncinate process
138 Head of pancreas, superior mesenteric vein, uncinate process
The uncinate process runs posteriorly around the mesenteric vein, coming between that vessel and the vena cava.
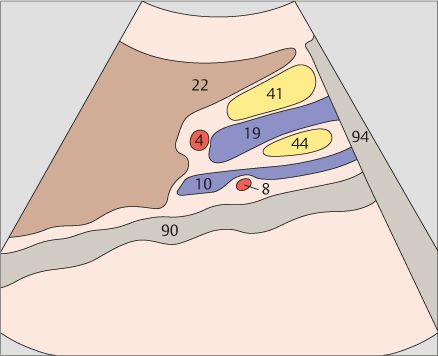
The superior mesenteric vein marks the boundary between the head and body of the pancreas.
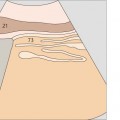
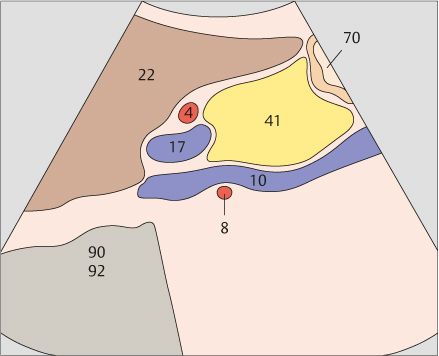
139 Body of pancreas, splenic vein
140 ody of pancreas, splenic vein, superior mesenteric artery, aorta
The body of the pancreas is the narrowest part of the organ in its ventrodorsal dimension.
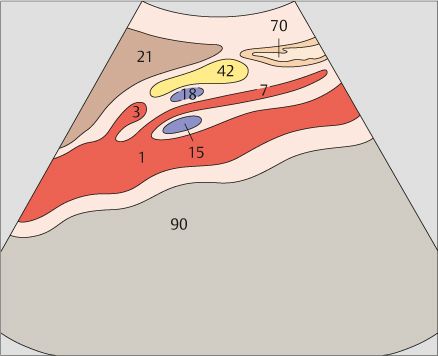
The celiac trunk is cranially adjacent to the body of the pancreas. The splenic vein and body of the pancreas cross over the superior mesenteric artery.
141 Body of pancreas, splenic vein
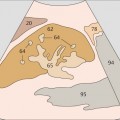
142 Tail of pancreas, splenic artery and vein, renal artery and vein
The left margin of the aorta marks the junction between the body and tail of the pancreas.
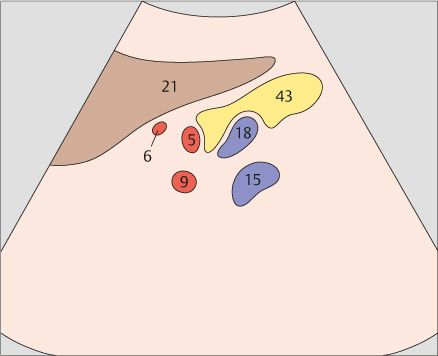
A longitudinal scan at the junction of the body and tail of the pancreas displays four vessels in cross section: the splenic artery, splenic vein, renal artery, and renal vein.
143 Tail of pancreas, splenic artery and vein, renal artery and vein
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree