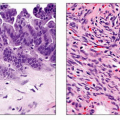
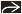Pancreatic Cysts
Brooke R. Jeffrey, MD
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Congenital, true, or epithelial pancreatic cyst
Refers to nonneoplastic, noninflammatory cysts
Imaging
Usually quite small (< 2 cm)
Round or oval shape, smooth thin wall, absence of internal complexity
Usually unilocular
Solitary or multiple (associated with cystic syndromes)
Syndromes account for most nonneoplastic cysts
von Hippel-Lindau disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney (ADPKD)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pancreatic pseudocyst
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma
Mucinous cystic pancreatic tumor
Pancreatic IPMN
Lymphangioma (mesenteric cyst)
Cystic islet cell tumor
Clinical Issues
“Simple” cyst ≤ 2 cm in asymptomatic adult is rarely of any clinical significance
Can follow with imaging, especially in elderly
Treatment: Clinical surveillance
Complete resection if endoscopic US or cyst aspiration suggests tumor
Diagnostic Checklist
Endoscopic US with needle aspiration is most accurate means of diagnosis
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Congenital, true, or epithelial pancreatic cyst
Definitions
Refers to nonneoplastic, noninflammatory cysts
IMAGING
General Features
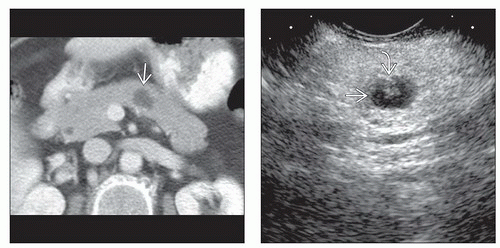
Best diagnostic clue
Simple-appearing cyst with no septa or mural nodularity in patients with no history of pancreatitis
Size
Usually quite small; giant cyst as large as 15 cm in diameter reported
Morphology
Round or oval shape, smooth thin wall, absence of internal complexity
Usually unilocular
Solitary or multiple (associated with cystic syndromes)
Radiographic Findings
ERCP: No connection between cyst and duct
CT Findings
Round lesion with water density contents
Thin, imperceptible wall
MR Findings
Hypointense on T1WI; hyperintense on T2WI
Ultrasonographic Findings
Anechoic; usually devoid of internal echoes
Imaging Recommendations