Pancreatic Solid and Pseudopapillary Neoplasm
Brooke R. Jeffrey, MD
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Imaging
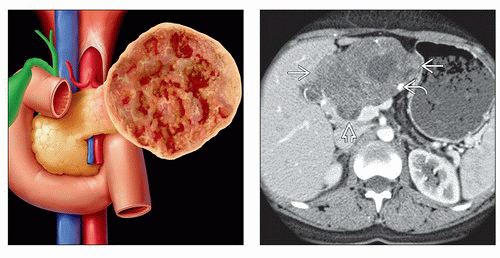
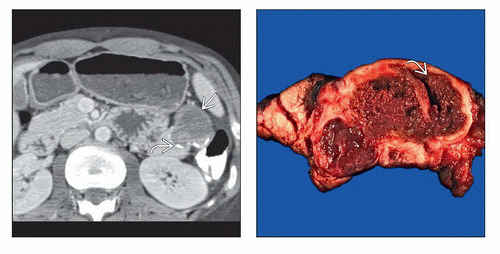
Encapsulated solid mass with cystic or hemorrhagic foci but no septation; in young women
Well-defined, heterogeneous, large mass
± calcification ( 5-10%)
Low-density areas of variable size within lesion; hemorrhage and necrosis
Thick, enhancing “capsule” (solid component)
± vascular invasion, metastases to liver, lymph nodes
Top Differential Diagnoses
Mucinous cystic pancreatic tumor
Spherical mass in body or tail of pancreas with several cystic spaces separated by thin septa
Most common in middle-aged to elderly women
Exophytic gastrointestinal stomal tumor
Pancreatic ductal carcinoma
Rarely necrotic or hemorrhagic
Obstructs pancreatic ± bile ducts
Older adults
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma
Typically has sponge appearance with innumerable small cysts
No large solid component
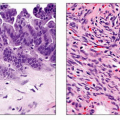
Pathology
Rare: < 3% of all pancreatic tumors
Low malignant potential (< 10% metastasize or recur)
Clinical Issues
< 35 years (rarely reported in older adults)
90% are women; often African-American
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm, papillary epithelial neoplasm, papillary cystic carcinoma, solid and cystic tumor of pancreas
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Encapsulated solid mass with cystic or hemorrhagic foci but no septation; in young women
Size
Average: 10 cm, range: 2.5-20 cm
CT Findings
CECT
Well-defined, heterogeneous, large mass
± calcification (5-10%)
Low-density areas of variable size within lesion; depends on degree of hemorrhage and necrosis
Thick, enhancing “capsule” (solid component)
± vascular invasion, metastases to liver, nodes
MR Findings
T1WI
Large, well-demarcated mass with central areas of low and high signal intensity (hemorrhage)
Capsule appears as rim of low intensity
Imaging Recommendations
Protocol advice
Multiplanar CECT or MR
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Mucinous Cystic Pancreatic Tumor
Most common in middle-aged to elderly women
Spherical mass in body or tail of pancreas with several cystic spaces separated by thin septa
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree