8 Pneumonia
Differential diagnosis
Clinical differentials to consider
• Pulmonary embolus – pleuritic chest pain/SOB/haemoptysis but sudden onset, usually no fever. The CXR is usually normal (see Chapter 24), but see also below.
Radiographic differentials
• Blood in the alveoli – traumatic contusion – should be easy to differentiate from pneumonia on clinical grounds.
• Tumour – bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. It can be radiologically indistinguishable from pneumonia. The difference is that it does not resolve with treatment.
Radiological features
Pneumonia can have several radiographic patterns. It can be confined to one lobe (lobar pneumonia) or be patchy and involve several lobes (bronchopneumonia). It can also cause a white-out of the hemithorax (see Chapter 9).
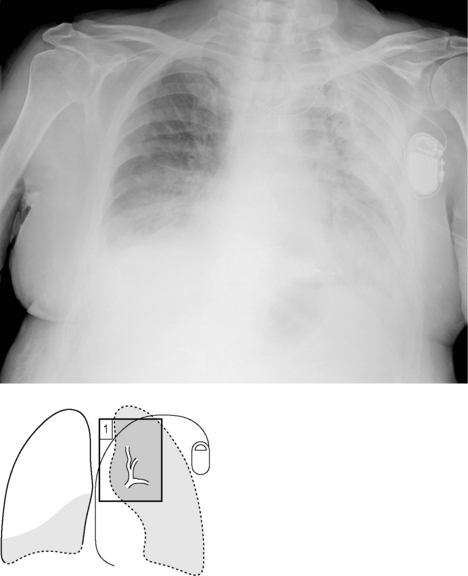
Fig. 8.1 is an example of both a white-out and right lower lobe pneumonia.
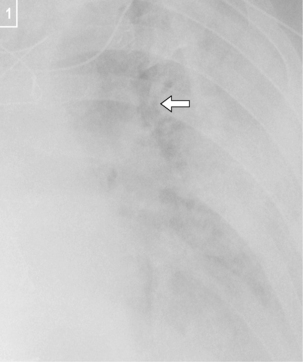
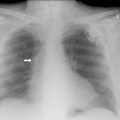
Fig. 8.1B The consolidation appears of increased density and is patchy. This is in contrast to collapses (Chapter 17) and pleural effusions (Chapter 20), which are more homogeneous. Consolidation may also contain air bronchograms (arrow). This is an exercise in understanding silhouette signs (see p. 5).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree