KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
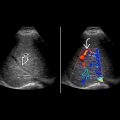
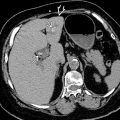
Intramural calcification of gallbladder (GB) wall, uncommon manifestation of chronic cholecystitis
Imaging
- •
Variable posterior acoustic shadowing dependent on quantity of calcification
- •
Complete: Thick, diffuse GB wall calcification
- ○
Hyperechoic semilunar line in GB fossa
- ○
Dense posterior acoustic shadowing
- ○
- •
Incomplete: Segmental GB wall calcification
- ○
Irregular (clumps) hyperechoic foci in GB wall
- ○
Biconvex curvilinear hyperechogenicity, less shadowing
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Gallstone-filled GB or large gallstone [wall-echo-shadow (WES) complex]
- •
Emphysematous cholecystitis
- •
Hyperplastic cholecystosis
Pathology
- •
Associated with gallstones in 95%
- •
Chronic inflammation/irritation leads to scarring, hyalinization, and dystrophic calcification
- •
Risk of GB cancer: 0-5% in incomplete type
- ○
Complete type: No risk, mucosa entirely denuded
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
Rare (< 0.1% at autopsy), more common in women (5:1)
- •
Usually occurs in 6th decade
- •
Typically asymptomatic; may have biliary-type pain
- •
Palpable, firm, nontender mass
Scanning Tips
- •
Optimize frequency and focus at level of GB to maximize depiction of calcification and posterior acoustic shadowing
- •
Look for soft tissue mass, indicating presence of GB carcinoma