, Joon Woo Lee1 and Eugene Lee2
(1)
Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, South Korea
(2)
Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, South Korea
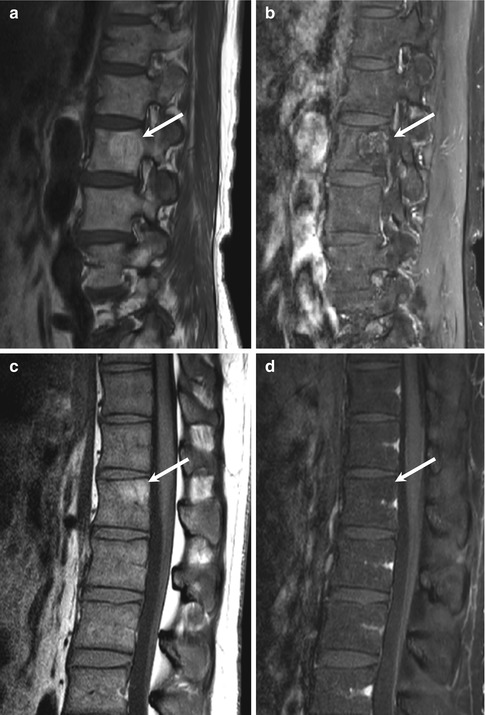
8.1 Focal Red Marrow Versus Metastasis
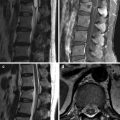
Focal red marrow (Fig. 8.1a, b) | Metastasis (Fig. 8.1c, d) | |
|---|---|---|
Similarities | Focal nodule Lower signal on T1-weighted image than that of surrounding fatty marrow Enhancement | |
Differences | Isointense or slightly hyperintense to the intervertebral disc on T1-weighted images Bright central area on T1-weighted images Patchy enhancement | Hypointense to the intervertebral disc on T1-weighted images No central fatty area Strong enhancement |

Fig. 8.1
8.2 Hemangioma Versus Benign Notochordal Cell Tumor (BNCT)
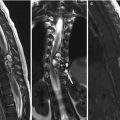
8.3 Aggressive Hemangioma Versus Metastasis
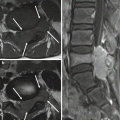
Aggressive hemangioma (Fig. 8.3a–c) | Metastasis (Fig. 8.3d–f) | |
|---|---|---|
Similarities | Osteolytic mass in the vertebral body Contrast enhancement on MRI | |
Differences | Thickened but preserved bony trabeculation Portion of T1-hyperintensity Round, Well-defined | Destructive bony trabeculation No area of T1-hyperintensity Poorly-defined |

Fig. 8.3
8.4 Hemangioma Versus Focal Fat Deposition
8.5 Metastasis Versus Schmorl’s Node
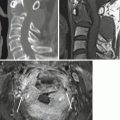
Metastasis (Fig. 8.5a, b) | Schmorl’s node (Fig. 8.5c, d) | |
|---|---|---|
Similarities | Focal nodular bony destruction in the vertebral body adjacent endplate Can be enhanced | |
Differences | Peripheral rim-like edema Stronger enhancement No continuity with intervertebral disc | Endplate disruption Continuity with intervertebral disc |