and Adam Sciuk2
(1)
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Resurrection Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA
(2)
Department of Radiology, Resurrection Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA
Abstract
Answers to Test #2 begin on page 120
Questions
1.
Which of the following cardiac imaging studies deliver the highest estimated effective radiation dose?
(A)
Rb-82 rest and stress
(B)
Calcium scoring
(C)
N-13 ammonia rest and stress
(D)
O-15 water rest and stress
2.
Quantitative bias that refers to the underestimation of counts density which differs from what they should be is called the partial-volume effect (PVE). Which of the following statements describing the PVE is TRUE?
(A)
PVE is more prominent in smaller tumor
(B)
PVE is more prominent in metastatic tumor
(C)
PVE is less prominent in tumor in situ
(D)
PVE is less prominent in bigger tumor
3.
Truncation is the source of streaking artifacts at the edge of the CT image. The presence of streaking artifacts:
(A)
Overestimates the attenuation coefficients
(B)
Produces image misregistration
(C)
Underestimates the attenuation coefficients
(D)
Necessitates use of shielding
4.
All of the following are the most commonly seen artifacts on PET/CT images EXCEPT:
(A)
Respiratory motion
(B)
Partial-volume effect
(C)
Truncation
(D)
Contrast medium
5.
The inverse of the mean distance traveled by photons before they deposit energy in the crystal is called:
(A)
The stopping power
(B)
Energy resolution
(C)
The decay constant
(D)
The light output
6.
Post-processing measures such as scaling, segmentation, or a combination of the two has been used in the PET/CT systems in order to:
(A)
Correct for scatter coincidences
(B)
Convert the CT attenuation coefficients to those corresponding to PET
(C)
Correct for random coincidences
(D)
Convert PET emission data to the CT attenuation coefficients
7.
The reconstruction method in which the comparison is made between the numerical projection data and the measured projection data in a feedback loop is called:
(A)
Filtered Back Projection (FBP)
(B)
Iterative Reconstruction (IR)
(C)
Ordered-Subset Expectation Maximization (OS-EM)
(D)
Maximum Likelihood—Expectation Maximization (ML-EM)
8.
Which of the following statements describing the role of PET in the diagnostic work-up of patients with melanoma is FALSE?
(A)
PET is a standard modality in evaluation of recurrent melanoma
(B)
Melanin content influences lesion detectability by PET
(C)
PET is most valuable in stage III disease
(D)
PET is more accurate for systemic staging than regional staging
9.
According to the Practice of Medicine and Pharmacy laws, all the clinical FDG-PET imaging work is complete by prescription by a physician and dispensing by registered:
(A)
Nurse
(B)
Radiologist
(C)
Pharmacist
(D)
Nuclear medicine physician
10.
If a radiopharmaceutical has a physical half-life of 110 min, and a biological half-life of 6 h, what is the effective half-life of the radiopharmaceutical in hours?
(A)
5.7 h
(B)
2 h
(C)
1.83 h
(D)
1.4 h
11.
Choose the correct interpretation of this ECG (Fig. 3.1):


Fig. 3.1
ECG Sample Case: A 59-year-old woman with shortness of breath
(A)
Normal sinus rhythm
(B)
Electronic ventricular pacemaker
(C)
Atrial fibrillation
(D)
Ventricular bigeminy
12.
The temporal improvement in contractile function of a dysfunctional myocardial region after restoration of blood flow describes:
(A)
Myocardial infarction
(B)
Myocardial viability
(C)
Diastolic dysfunction
(D)
Systolic dysfunction
13.
Linear attenuation coefficient determines the scintillator:
(A)
Stopping power
(B)
Energy resolution
(C)
Decay constant
(D)
Light output
14.
Administration/consumption of which of the following before F-18 FDG dosing will DECREASE uptake of the radiotracer by BAT (Brown Adipose Tissue)?
(A)
Ephedrine
(B)
Propranolol
(C)
Caffeine
(D)
Nicotine
15.
The breathing protocols applied during PET/CT acquisition, e.g., respiratory gating, the breath-hold at inspiration protocol, and the shallow breathing protocol are utilized to eliminate:
(A)
Truncation artifacts
(B)
Misregistration artifacts
(C)
Contrast media artifacts
(D)
Streaking artifacts
16.
In which of the following clinical circumstances is the application of standardized uptake value (SUV) most likely to be useless?
(A)
Prognosis of the disease
(B)
Diagnosis of the disease
(C)
Staging of the disease
(D)
Therapy monitoring of the disease
17.
Which of the following scintillators is commercially available in a time-of-flight (TOF) PET imaging?
(A)
GSO
(B)
BaF2
(C)
BGO
(D)
LYSO
18.
Administration of water-equivalent contrast agent when performing PET/CT imaging:
(A)
Underestimates SUV
(B)
Overestimates SUV
(C)
Does nOt affect SUV
(D)
Produces streaking artifacts
19.
The presented PET MIP image in Fig. 3.2 was obtained in routine PET/CT examination. Which of the following expressions can be found in the body of the radiologist’s report describing the exam’s findings?


Fig. 3.2
PET/CT examination
(A)
Hypermetabolic activity in the infracarinal region…increased activity in both adrenal glands…
(B)
Mass at the right lung base with rim of increased activity…increased activity in the left adrenal…
(C)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci….liver metastases
(D)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci…physiologic uptake in the abdomen and pelvis
20.
Calculate a 14-year-old child’s dose for a PET scan using Webster’s formula with the following parameters:
Adult dose—13 mCi
Child’s weight—149 lb
Child’s height—5′ 6″
(A)
5.7 mCi
(B)
7.0 mCi
(C)
9.2 mCi
(D)
12.6 mCi
21.
A state of chronically reduced contractility in viable myocardial tissue, caused by prolonged or repetitive reductions in myocardial flow, is called:
(A)
Scarred myocardium
(B)
Ischemic myocardium
(C)
Stunned myocardium
(D)
Hibernatic myocardium
22.
The 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) of American Heart Association (AHA) recommend in adults a compression depth of at LEAST:
(A)
1 in.
(B)
1.5 in.
(C)
2 in.
(D)
2.5 in.
23.
If a truncated CT scan is used for the attenuation correction of a larger transaxial field of view PET scan, the activity estimates outside the measured CT field of view will be:
(A)
Underestimated
(B)
Overestimated
(C)
Unchanged
(D)
Equal to 0
24.
A global reduction in the brain function assessed by F-18 FDG uptake is observed in:
(A)
Dementia
(B)
Parkinson’s disease
(C)
Hypothyroidism
(D)
Hyperthyroidism
25.
Medicare reimbursement for PET-FDG Myocardial Viability imaging is available in all of the following settings EXCEPT:
(A)
Primary diagnosis
(B)
Following an inconclusive SPECT
(C)
Initial diagnosis
(D)
Following an inconclusive CCTA
26.
The histological presence of extracellular β-amyloid plaques (Aβ) and intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in the cerebral cortex defines:
(A)
Parkinson’s disease
(B)
Alzheimer’s disease
(C)
Dementia
(D)
Glioma
27.
In the typical PET/CT acquisition, the CT component is performed as:
(A)
A non-contrast low radiation dose scan
(B)
A non-contrast high radiation dose scan
(C)
High radiation dose scan with a contrast
(D)
Low radiation dose scan with a contrast
28.
Ovarian uptake of F-18 FDG in a postmenopausal patient indicates:
(A)
A normal finding
(B)
Malignancy
(C)
Pregnancy
(D)
Ovulating ovary
29.
Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals has been developed as the PET tracer to measure a cell proliferation rate?
(A)
F-18 fluoride
(B)
C-11 Pittsburg compound
(C)
C-11 acetate
(D)
F-18 fluorothymidine
30.
Calculate the percent error using the following results obtained from the geometry test on the dose calibrator:
Reference 4 ml volume reading is 1.9 mCi
Actual 20 ml volume reading 1.68 mCi
(A)
13.1%
(B)
11.6%
(C)
−3.1%
(D)
−6.8%
31.
Figure 3.3 is a routine cardiogram from a hospitalized patient. Interpret this tracing.


Fig. 3.3
ECG Sample Case: A 69-year-old woman with heart palpitations
(A)
Normal sinus rhythm
(B)
Electronic ventricular pacemaker
(C)
Atrial fibrillation
(D)
Ventricular bigeminy
32.
An area of focal FDG uptake in the lungs, without corresponding finding on CT scan, can be caused by all of the following EXCEPT:
(A)
An injected blood clot
(B)
Motion artifact
(C)
Pulmonary infarction
(D)
Contamination
33.
The main stream of X-ray photons generated in the X-ray tube is described as:
(A)
Braking radiation
(B)
Characteristic radiation
(C)
Compton scattering
(D)
Attenuation photons
34.
A group of ROIs through planes, which define a three-dimensional region of relevance, is called:
(A)
Volume of interest
(B)
Maximum-intensity projection
(C)
Multiplanar reconstruction
(D)
Dose uptake ratio
35.
Coincidence events registered in PET acquisition and defined as prompt counts include:
(A)
True and scatter events
(B)
Scatter and randoms
(C)
True and randoms
(D)
True, scatter, and randoms
36.
An analytic reconstruction algorithm that assigns the values in the projection to all points along the line of acquisition through the image plane from which they were acquired is known as:
(A)
Filtered back projection
(B)
Back projection
(C)
Iterative reconstruction
(D)
Filtering
37.
Quality control testing for PET agents that involves decay analysis in a dose calibrator for a defined period of time is called:
(A)
Specific activity analysis
(B)
Radiochemical purity
(C)
Radionuclidic identity
(D)
Bacterial endotoxin testing
38.
The following are examples of oral hypoglycemic drugs EXCEPT:
(A)
Metformin
(B)
Glyburide
(C)
Dicumarol
(D)
Chlorpropamide
39.
C-11 L-leucine, C-11 L-methionine, and C-11 L-tyrosine were developed as the PET tracers to assess:
(A)
Membrane synthesis
(B)
Lipids metabolism
(C)
Hypoxia extent
(D)
Protein synthesis
40.
Which of the following patient’s medications can be responsible for the findings presented on the coronal maximum-intensity projection PET image (Fig. 3.4)?


Fig. 3.4
PET/CT examination
(A)
Metformin
(B)
Lasix
(C)
Propranolol
(D)
Valium
41.
Decreased myocardial blood flow combined with decreased myocardial glucose metabolism indicates the presence of:
(A)
Normal viable myocardium
(B)
Nonviable myocardium
(C)
Stunned myocardium
(D)
Hibernating myocardium
42.
The parietal lobe of the brain is located behind the frontal lobe and controls:
(A)
Auditory information
(B)
Visual information
(C)
Smell sensation
(D)
Tactile sensation
43.
The PET scanner quality control procedure in which data are used to compensate for the variation in efficiency in each line of response (LOR) in the sinogram is called:
(A)
Normalization
(B)
Calibration
(C)
Blank scan
(D)
Attenuation correction
44.
The following statements correctly describe the standardized uptake value (SUV) in reconstructed PET images EXCEPT:
(A)
Quantitative accuracy for data acquired in the 2D is higher than that in the 3D
(B)
Emission data require correction for the presence of random coincidences
(C)
The background noise in data acquired in the 2D is higher than that in the 3D
(D)
Emission data require correction for the presence of scatter coincidences
45.
The total attenuation is the sum of the attenuation due to different types of interactions and includes all of the following EXCEPT:
(A)
The photoelectric effect
(B)
The Compton scattering
(C)
The pair production
(D)
Bremsstrahlung radiation
46.
If the collected data follow a Gaussian distribution, 68% of gathered values will be within:
(A)
One standard deviation
(B)
Two standard deviations
(C)
Three standard deviations
(D)
Mean +/−10
47.
The parameter of the CT scanner defined as the ratio of the table feed per gantry rotation to the total X-ray beam width is called:
(A)
Pitch
(B)
Bed
(C)
Ring
(D)
Hybrid
48.
A substitution radioactive for nonradioactive element in a biologically active PET tracer molecule without altering its biologic properties is called:
(A)
Hot-for-hot substitution
(B)
Cold-for-hot substitution
(C)
Hot-for-cold substitution
(D)
Cold-for-cold substitution
49.
F-18 fluoroestradiol (FES) was developed as the PET tracer to assess:
(A)
Membrane synthesis
(B)
Estrogen receptor
(C)
Hypoxia extent
(D)
Protein synthesis
50.
How many atoms disintegrating per second are measured by one becquerel?
(A)
1,000
(B)
100
(C)
10
(D)
1
51.
Which of the following statements describing properties of the survey meters routinely used in the NM departments is FALSE?
(A)
A cutie-pie counter is an ionization chamber
(B)
A Geiger–Mueller counter is used for low level surveys
(C)
A Geiger–Muller counter output is proportional to the exposure rate
(D)
A cutie-pie output is proportional to the total energy deposited
52.
The accessory organs of the digestive system include the:
(A)
Esophagus
(B)
Stomach
(C)
Liver
(D)
Small intestine
53.
A linear transformation of the initial linear attenuation coefficient measurement into one in which the radiodensity of distilled water and the radiodensity of air at standard pressure and temperature (STP) is equal to 0 and −1,000 accordingly is called:
(A)
Hounsfield unit scale
(B)
Attenuation coefficient
(C)
Partial voluming
(D)
Beam hardening
54.
The capacity to overlay data from distinct sources that will map a pixel from one source into a pixel from the other is called:
(A)
Image attenuation
(B)
Image registration
(C)
Filtering
(D)
Rebining
55.
Two photons arising from two annihilation events and detected within each other’s coincidence window are:
(A)
True coincidences
(B)
Random events
(C)
Scatter coincidences
(D)
Single events
56.
The following tests can be used to assess the ability of the device to reproducibly records detected events EXCEPT:
(A)
Chi-square test
(B)
Poisson standard deviation
(C)
Gaussian standard deviation
(D)
Student’s t-test
57.
The dose calibrator quality control procedure performed with different sealed radionuclides is called:
(A)
Geometry
(B)
Accuracy
(C)
Linearity
(D)
Constancy
58.
Which of the following radionuclides commonly used in PET imaging has the lowest positron range in water?
(A)
Carbon-11
(B)
Nitrogen-13
(C)
Oxygen-15
(D)
Fluorine-18
59.
The Cotswold system (formerly the Ann Arbor Staging System) applies to both Hodgkin’s disease (HD) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) and divides them into:
(A)
2 stages
(B)
4 stages
(C)
6 stages
(D)
8 stages
60.
The diagram for the process of positron–electron annihilation is shown in the Fig. 3.5. Which of the following labels identifies the positron-emitting nucleus?


Fig. 3.5
Positron–electron annihilation diagram. Illustration by Sabina Moniuszko
(A)
D
(B)
C
(C)
B
(D)
A
61.
When handling a minor radioactive spill the technologists should perform the following sequence of events:
(A)
Decontaminate personnel, survey the area, notify a supervisor
(B)
Write up report, contain the spill, notify the RSO
(C)
Clear the area, notify a supervisor, contain the spill
(D)
Decontaminate personnel, clear the area, write up report
62.
Which of the following histopathological types of the gastric carcinoma is associated with the low F-18 FDG uptake?
(A)
Tubular carcinoma
(B)
Papillary carcinoma
(C)
Signet-ring cell carcinoma
(D)
Metastatic adenocarcinoma
63.
Which of the following scintillators commonly used in PET has the highest light output?
(A)
LSO (lutetium oxyorthosilicate)
(B)
BaF2 (barium fluoride)
(C)
BGO (bismuth germinate)
(D)
GSO (gadolinium orthosilicate)
64.
Low carbohydrate and a high protein diet favor the metabolism of:
(A)
Carbohydrates
(B)
Ketones
(C)
Amino acids
(D)
Fatty acids
65.
The energy of the X-ray photons produced by the CT X-ray tube is controlled by the:
(A)
The tube voltage (kV)
(B)
The temperature of the anode
(C)
The tube current (mA)
(D)
The temperature of the cathode
66.
Urinary bladder catheterization prior to PET imaging might be required for patients diagnosed with:
(A)
Pulmonary nodule
(B)
Brain tumor
(C)
Melanoma
(D)
Uterine carcinoma
67.
Which of the following statements describing F-18 FDG uptake in gallbladder/biliary tract is FALSE?
(A)
No uptake is observed in normal GB wall
(B)
GB wall uptake is seen in acute cholecystitis
(C)
Focal GB uptake is observed in GB carcinoma
(D)
Cholestasis can cause false-negative liver lesions
68.
In the process of differentiation between residual viable or recurrent tumor and radiation necrosis in patients with treated primary or metastatic CNS brain tumor, absence of FDG uptake in the region of interest indicates:
(A)
Brain tumor
(B)
Brain tumor and radiation necrosis
(C)
Radiation necrosis
(D)
Neither brain tumor nor radiation necrosis
69.
Which of the following statements describing the clinical utility of PET/CT-FDG imaging vs. PET-FDG imaging is FALSE?
(A)
FDG-PET/CT has less of a tendency toward upstaging of patients than FDG-PET alone
(B)
FDG-PET/CT correctly downstages a number of patients compared with FDG-PET alone
(C)
FDG-PET/CT has more false-positive findings than FDG-PET alone
(D)
FDG-PET/CT is found to be more accurate for staging than FDG-PET alone
70.
In the image in Fig. 3.6 shown below, what structure is depicted by line “c”?


Fig. 3.6
CT anatomy, transaxial
(A)
Right ventricle
(B)
Liver
(C)
Left ventricle
(D)
Aorta
71.
What sign should be posted in an area accessible to personnel in which a major portion of the body of a person could receive a dose in excess of 100 mrem in 1 h?
(A)
Radioactive materials
(B)
Radiation area
(C)
High radiation area
(D)
Airborne radioactivity area
72.
The three main divisions of the large intestine are the:
(A)
Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
(B)
Cecum, colon, and rectum
(C)
Cecum, colon, and ileum
(D)
Duodenum, jejunum, and rectum
73.
The following methods are employed in the quantitative PET F-18 FDG studies EXCEPT:
(A)
Tumor-to-background ratios
(B)
Signal-to-noise ratios
(C)
Standardized uptake values
(D)
Full kinetic analysis
74.
A group of naturally occurring glycoproteins that regulates the production, differentiation, survival, and activation of hematopoietic cells are called:
(A)
Mucins
(B)
Immunoglobulins
(C)
Colony-Stimulating Factors (CSFs)
(D)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
75.
PET images that are distinguished by “hot skin” and the manifestation of the lungs with high tracer uptake and the low tracer concentrations in the mediastinum are:
(A)
Non-attenuation-corrected (NAC) images
(B)
Attenuation-corrected (AC) images
(C)
Maximum-intensity projection (MIP) images
(D)
Attenuation-corrected (AC) or non-attenuation-corrected (NAC) images
76.
The pharmacological effect of dipyridamole or adenosine can be reversed by the administration of:
(A)
Propranolol
(B)
Valium
(C)
Aminophylline
(D)
Nitroglycerine
77.
Which of the following statements describing different methods of SUV normalization is FALSE?
(A)
SUV can be normalized to total body mass
(B)
SUV can be normalized to lean body mass
(C)
SUV can be normalized to body surface area
(D)
SUV normalization based on total body mass is the most dependable
78.
The occipital lobe is located in the posterior part of the brain and is responsible for the processing of:
(A)
Auditory information
(B)
Visual information
(C)
Smell sensation
(D)
Tactile sensation
79.
Which of the following histological types of thyroid carcinoma DOES NOT concentrate iodine?
(A)
Classic papillary
(B)
Classic follicular
(C)
Papillary encapsulated
(D)
Anaplastic
80.
The energy imparted to a unit mass of matter by ionizing radiation is measured in:
(A)
Rad
(B)
Rem
(C)
Curie
(D)
Roentgen
81.
N-13 ammonia demonstrates extended myocardial retention, by staying metabolically trapped within the myocytes. This is due to:
(A)
Activity of the Na/K-ATPase pumps
(B)
Binding to the mitochondrial complex
(C)
The glutamine synthetase pathway
(D)
Glucose transporters activity
82.
Bilateral, symmetric decreased FDG uptake in the temporoparietal region of the brain is the prevailing pattern observed in:
(A)
Pick disease
(B)
Vascular dementia
(C)
Alzheimer’s disease
(D)
Dementia with Lewy bodies
83.
The presented PET-MIP image in the Fig. 3.7 was obtained in routine PET/CT examination. Which of the following expressions can be found in the body of the radiologist’s report describing the exam’s findings?


Fig. 3.7
PET/CT examination
(A)
Hypermetabolic activity in the infracarinal region…physiologic bladder activity…..
(B)
Mass at the right lung base with rim of increased activity…increased activity in the left adrenal…
(C)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci….liver metastases
(D)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci…physiologic uptake in the abdomen and pelvis
84.
A clinically significant incidence of febrile neutropenia after myelosuppressive chemotherapy is a common indication for treatment with:
(A)
Erythropoietin
(B)
Thrombopoietin
(C)
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)
(D)
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
85.
According to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST), complete response to therapy is defined as a disappearance of all tumor foci for at least:
(A)
1 week
(B)
2 weeks
(C)
4 weeks
(D)
8 weeks
86.
Brain metabolism and blood flow are increased at the site of onset of the seizure in the:
(A)
Interictal state
(B)
Intraictal state
(C)
Inter and intraictal states
(D)
Neither inter or intraictal states
87.
A type of beta decay in which a proton is converted to a neutron and the antimatter counterpart of an electron and a neutrino are released is called:
(A)
Positron emission
(B)
Isomeric transition
(C)
Electron capture
(D)
Beta (-) decay
88.
Which of the following tests is the basis of screening as well as a useful tool in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer?
(A)
Barium enema
(B)
Occult blood testing
(C)
Sigmoidoscopy
(D)
Colonoscopy
89.
Reimbursable by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services oncologic applications for PET scanning in lymphoma management include all of the following EXCEPT:
(A)
Diagnosis
(B)
Staging
(C)
Therapy monitoring
(D)
Restaging
90.
The event illustrated in the diagram in Fig. 3.8 is called:


Fig. 3.8
Principle of positron emission imaging. Illustration by Sabina Moniuszko
(A)
A random event
(B)
A scatter event
(C)
A true event
(D)
An attenuated event
91.
The excretion of Ga-68 DOTA-peptides is primarily through the:
(A)
Skin
(B)
Bowel
(C)
Gallbladder
(D)
Kidney
92.
Nigral degeneration and striatal dopamine deficiency are characteristic findings present in:
(A)
Parkinson’s disease (PD)
(B)
Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
(C)
Vascular dementia
(D)
Ictal epilepsy
93.
The difference in the detection times between two coincidence photons that is used to determine most likely location of the annihilation event along LOR is applied in:
(A)
Hybrid imaging
(B)
Time-of-flight imaging
(C)
Image coregistration
(D)
Scatter correction
94.
The single most important prognostic factor in patients with colon cancer is/are:
(A)
Metastases to regional lymph nodes
(B)
The location of the carcinoma
(C)
The size of the lesion
(D)
Coexisting diseases
95.
Extending the axial FOV of the scanner to cover the patient more in a single-bed position results in:
(A)
Increased sensitivity
(B)
The decreased rates of scatter
(C)
The decreased rates of randoms
(D)
Increased resolution
96.
Which of the following is the most common risk factor for colorectal cancer?
(A)
Smoking
(B)
Drinking
(C)
A family history
(D)
Uncontrolled diabetes
97.
A pencil shape, a fan shape, and a cone shape are common terms used in radiography to describe:
(A)
CT detectors arrangements
(B)
CT detectors properties
(C)
X-ray beam
(D)
X-ray tube
98.
A normal endometrial uptake F-18 FDG is most commonly seen:
(A)
During ovulation
(B)
During menstruation
(C)
A few days before the menstrual flow
(D)
A few days after the menstrual flow
99.
F-18 flurpiridaz is a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging tracer that has been explored in patients with:
(A)
Lymphoma
(B)
Malignant melanoma
(C)
Coronary artery disease
(D)
Non-small cell carcinoma
100.
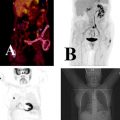
The presented images in Fig. 3.9 labeled A, B, C, and D were obtained during a routine CT of the head. The image described as A represents:


Fig. 3.9
Brain CT scans
(A)
Lateral head localizer image
(B)
Coronal slice of the brain
(C)
Saggital slice of the brain
(D)
Tranverse slice of the brain
101.
A hypothetical aggregation of human physical and physiological characteristics arrived at by international consensus is called:
(A)
Average man
(B)
Average worker
(C)
Reference man
102.
Diaphragmatic crus F-18 FDG uptake can be seen in patients with:
(A)
Tachycardia
(B)
Increased respiratory effort
(C)
Anxiety
(D)
Excessive sweating
103.
In the test–retest setting, the reproducibility of quantitative PET parameters depends mainly on:
(A)
ROI and lesion size
(B)
Glucose correction factors
(C)
The reconstruction method
(D)
Body weight correction factors
104.
The recommended time interval necessary to avoid increased FDG uptake in the spleen and bone marrow after granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) therapy is at least:
(A)
1 day
(B)
1 week
(C)
10 days
(D)
4 weeks
105.
With regard to nodal lesions detection in patients with lymphoma, non-attenuation-corrected (NAC) PET images are superior to attenuation-corrected (AC) PET images in evaluating:
(A)
The deeply seated nodal lesions
(B)
The superficial nodal lesions
(C)
The anteriorly seated nodal lesions
(D)
The posterior nodal lesions
106.
Segmental colon activity observed on PET F-18 FDG scan suggests:
(A)
Colon carcinoma
(B)
Colon polyp
(C)
Colon inflammation
(D)
Colon metastases
107.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Which of the following preparations can be used if intravenous hydration before F-18 FDG imaging is indicated?
(A)
Dextrose