and Adam Sciuk2
(1)
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Resurrection Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA
(2)
Department of Radiology, Resurrection Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA
Abstract
Answers to Test #3 begin on page 191
Questions
1.
Which of the following cardiac imaging studies deliver the lowest estimated effective radiation dose?
(A)
Rb-82 rest and stress
(B)
CT attenuation correction
(C)
N-13 ammonia rest and stress
(D)
O-15 water rest and stress
2.
Recovery coefficient, Geometric Transfer Matrix, and Deconvolution technique are modification methods employed in:
(A)
Attenuation calculation
(B)
Scatter correction
(C)
Partial-volume effect correction
(D)
Attenuation measurement
3.
The number of electrons discharged from the cathode filament is controlled by the:
(A)
The tube voltage (kV)
(B)
The temperature of the anode
(C)
The tube current (mA)
(D)
The distance from the target
4.
Which of the following are the most common artifacts in PET/CT imaging?
(A)
Truncation artifacts
(B)
Motion artifacts
(C)
Contrast medium artifacts
(D)
Metallic implants artifacts
5.
The PET scanner quality control procedure in which data are used to convert the reconstructed image pixel values into activity concentration is called:
(A)
Normalization
(B)
Calibration
(C)
Blank scan
(D)
Attenuation correction
6.
Post-processing technique performed on CT images that involves reformatting of cross-sectional images to produce images of the outsides of anatomical structures is called:
(A)
Multiplanar reconstruction
(B)
3D surface rendering
(C)
Cone beam reconstruction
(D)
Back projection
7.
ALL of the following statements describing the usefulness of PET-FDG imaging in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) are correct EXCEPT:
(A)
High physiologic background activity in urine limits scan interpretation accuracy
(B)
Metastatic RCC has more intense FDG uptake compared with the primary
(C)
Primary RCC has more intense FDG uptake compared with the metastatic
(D)
The administration of furosemide can be beneficial for reducing false-negative scan results
8.
The reconstruction algorithm that reduces the unnecessary 3D data to a stack of independent 2D sonograms, which can then be reconstructed using either 2D filtered back projection (FBP) or 2D iterative algorithms, is called:
(A)
Fourier transform
(B)
Convolution
(C)
Filtering
(D)
Fourier rebinning
9.
The patented PET tracers that have been developed by a radiopharmaceutical developer or manufacturer are called:
(A)
Proprietary agents
(B)
Research agents
(C)
Nonproprietary agents
(D)
Contrast agents
10.
A patient is scheduled to have PET myocardial perfusion imaging using Rb-82 as a tracer of choice. The technologist draws up a 42-mCi dose of Rb-82 for the resting injection at 10:00 a.m. If the injection is delayed 3 min, how many milicuries of Rb-82 will be remaining in the syringe at 10:03 a.m.?
(A)
48 mCi
(B)
26 mCi
(C)
8 mCi
(D)
6 mCi
11.
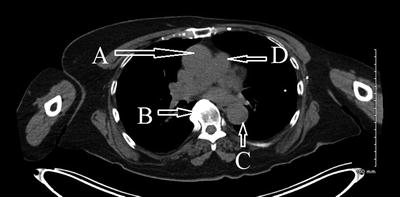
The display shown in Fig. 4.1 presents attenuation-corrected and reconstructed positron emission tomography (PET-FDG) viability study. The reoriented tomographic slices are:
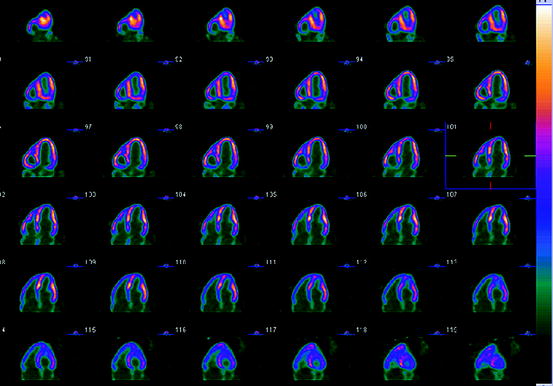

Fig. 4.1
PET/CT-FDG viability study
(A)
Short-axis slices
(B)
Vertical long-axis slices
(C)
Oblique short-axis slices
(D)
Horizontal long axis
12.
The following are examples of molecular and functional alterations occurring in cancer tissue EXCEPT:
(A)
Increased protein synthesis
(B)
Increased angiogenesis
(C)
Increased oxygen tension
(D)
Increased glucose metabolism
13.
Which of the following types of cardiac scanning processing requires performance of blood pool subtraction?
(A)
Imaging using water O-15
(B)
Imaging using rubidium Rb-82
(C)
Imaging using acetate C-11
(D)
Imaging using ammonia N-13
14.
Which of the following halogens most closely mimics the size of the hydrogen atom?
(A)
Br-2
(B)
Cl-2
(C)
F-2
(D)
I-2
15.
Two photons arising from the same annihilation event and detected along two different lines of response (LOR) are:
(A)
True coincidences
(B)
Random events
(C)
Scatter coincidences
(D)
Single events
16.
PET/CT imaging artifact described as a liver lesion that can inaccurately become visible at the base of the lung and mimics a lung nodule is produced by:
(A)
Contrast medium
(B)
Respiratory motion
(C)
Patient motion
(D)
Dose extravasation
17.
Which of the following physical properties of different scintillators describe LSO (lutetium oxyorthosilicate) detector?
(A)
Attenuation coefficient—0.96, relative light output—15, decay time—300 ns
(B)
Attenuation coefficient—0.87, relative light output—75, decay time—40 ns
(C)
Attenuation coefficient—0.35, relative light output—100, decay time—230 ns
(D)
Attenuation coefficient—0.44, relative light output—5, decay time—0.6 ns
18.
Which of the following statements describing brown adipose tissue (BAT) is TRUE?
(A)
BAT is richly innervated by parasympathetic nerves
(B)
BAT is not present in newborns
(C)
BAT primary function is to generate body heat
(D)
BAT contains cells rich in ribosomes
19.
Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals has been developed as the PET tracer to measure a membrane lipid synthesis?
(A)
F-18 fluoride
(B)
F-18 fluorocholine
(C)
F-18 fluoroestradiol
(D)
F-18 fluorothymidine
20.
The molecular imaging strategy that replicates the downstream physiological effects of one or more molecular or genetic processes is called:
(A)
Direct molecular imaging
(B)
Surrogate molecular imaging
(C)
Indirect molecular imaging
(D)
Reporter gene imaging
21.
Which of the following detectors that have been used in PET imaging is intrinsically radioactive?
(A)
LSO (lutetium oxyorthosilicate)
(B)
BaF2 (barium fluoride)
(C)
BGO (bismuth germinate)
(D)
GSO (gadolinium orthosilicate)
22.
In which of the following types of seizures consciousness is not impaired?
(A)
Partial complex seizures
(B)
Partial simple seizures
(C)
Petit mal seizures
(D)
Grand mal seizures
23.
Mean sensitivity and specificity of PET myocardial perfusion studies for the detection of coronary artery disease (CAD) are accordingly:
(A)
93% and 50%
(B)
93% and 92%
(C)
50% and 92%
(D)
50% and 50%
24.
Hot-for-cold substitution is applied in the development process of all of the following PET tracers EXCEPT:
(A)
Carbon-11
(B)
Oxygen-15
(C)
Nitrogen-13
(D)
Fluorine-18
25.
The pattern of FDG uptake in multi-infarct dementia is characterized by:
(A)
The parietotemporal hypometabolism
(B)
The visual cortices involvement
(C)
The frontotemporal regions involvement
(D)
Scattered regions of hypometabolism
26.
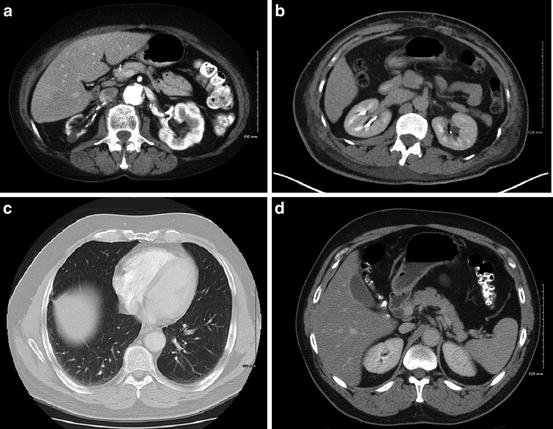
The presented PET MIP, fused PET/CT, and CT axial images in Fig. 4.2 were obtained from the patient referred for the evaluation of abdominal mass. Based on the findings the abdominal mass represents:
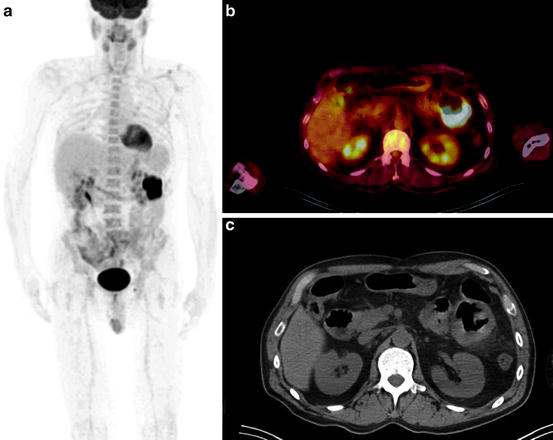

Fig. 4.2
(a) PET MIP image; (b) PET/CT image; (c) CT image
(A)
Metastatic cancer of the liver
(B)
Solid tumor of the left kidney
(C)
Cavitary mass arising from the left kidney
(D)
Cavitary mass adjacent to small bowel
27.
Any chest area that specially attenuates the x-ray beam and as a result appears more dense than the surrounding region is called:
(A)
Plaque
(B)
Opacity
(C)
Atelectasis
(D)
Pneumonia
28.
The area of maximal electrophysiological interictal activity is called:
(A)
The brain infarct
(B)
The epileptic focus
(C)
The epileptogenic lesion
(D)
The brain ischemia
29.
Fluoromisonidazole (F-18 MISO) was developed as the PET tracer to assess:
(A)
Membrane synthesis
(B)
Lipids metabolism
(C)
Hypoxia extent
(D)
Protein synthesis
30.
Two patients are scheduled to have PET myocardial perfusion imaging at 8:00 a.m. and 8:20 a.m., each with dose of 15 mCi Nitrogen-13-ammonia. What is the total millicurie amount that should be available at 7:30 a.m. to accommodate these two studies?
(A)
600 mCi
(B)
480 mCi
(C)
120 mCi
(D)
36 mCi
31.
Which of the following statements describing hypoxia in a growing tumor is FALSE?
(A)
Hypoxia inhibits cell proliferation
(B)
Hypoxia promotes cells adaptive responses
(C)
Hypoxia “guards” cells from the cytotoxic effects of radiation
(D)
Hypoxia is independent from the local vasculature
32.
Normal, focal ureteral activity can be seen in:
(A)
The lower pelvis
(B)
The lower abdomen
(C)
The superior pelvis
(D)
The superior abdomen
33.
Computed tomography acquisition (CT) performed by acquiring unenhanced CT images first, followed by a series of CT images after intravenous injection of contrast medium, is called:
(A)
Unenhanced CT with a low-dose technique
(B)
Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) CT
(C)
Dual energy CT
(D)
Multislice CT
34.
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) has bilateral temporoparietal decreased FDG uptake similar to that present in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and also involves:
(A)
The frontal lobe
(B)
The occipital lobe
(C)
The cerebellum
(D)
The basal ganglia
35.
The main objective of Bayesian analysis is to combine both clinical and imaging-based characteristics to obtain an assessment of the:
(A)
Cost of treatment
(B)
Time of recovery
(C)
Probability of disease
(D)
Longtime prognosis
36.
Radiation effects on bone marrow affecting FDG uptake can be described as:
(A)
Increased uptake in the area of spine
(B)
Increased area of uptake corresponding to the radiation field
(C)
Decreased uptake in the area of spine
(D)
Decreased area of uptake corresponding to the radiation field
37.
Hybrid PET-CT scanners, equipped with multislice CT, can be used to perform the following types of cardiac diagnostic imaging EXCEPT:
(A)
PET myocardial perfusion study
(B)
Coronary angiography
(C)
Echocardiography
(D)
Calcium scoring
38.
The sphincter muscle that protects the opening of the esophagus into the stomach is called the:
(A)
Pyloric sphincter
(B)
Esophageal sphincter
(C)
Sphincter of Oddie
(D)
Sphincter ani
39.
The consequences of the mesothelioma stage on treatment selection depend entirely on whether:
(A)
Chemotherapy will be a treatment possibility
(B)
Surgical intervention will be a treatment possibility
(C)
Radiotherapy will be a treatment possibility
(D)
Radioimmunotherapy will be a treatment possibility
40.
A package of several F-18 FDG unit doses is reading 19.5 mR/h. How many half value layers of lead (Pb) should be placed in front of the package to reduce the exposure to a background level of 0.03 mR/h?
(A)
38.5 HVLs
(B)
9.4 HVLs
(C)
4-1 HVLs
(D)
2.8 HVLs
41.
The amount of radioactivity, for gamma and beta radiation, measured with wipe tests on the packages designated White I, Yellow II, or Yellow III Department of Transportation DOT labels, should not EXCEED:
(A)
2.2 dpm/cm2
(B)
22 dpm/cm2
(C)
222 dpm/cm2
(D)
2,222 dpm/cm2
42.
The most common site for distant metastases of the colorectal cancer is:
(A)
The lung
(B)
The brain
(C)
The liver
(D)
He spleen
43.
According to the Cotswold system (formerly the Ann Arbor Staging System), involvement of lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm describes:
(A)
Stage I of lymphoma
(B)
Stage II of lymphoma
(C)
Stage III of lymphoma
(D)
Stage IV of lymphoma
44.
The main physicochemical property of a PET radiotracer that decides its ability to enter the brain and label the target receptor or enzyme is:
(A)
The lipophilicity of the complex
(B)
The hydrophilicity of the complex
(C)
The molecular mass of the complex
(D)
The electrical charge of the complex
45.
Cardiac PET quantification of myocardial blood flow (MBF) and coronary flow reserve (CFR) may be useful for detection and evaluation of all of the following EXCEPT:
(A)
Left ventricle ejection fraction
(B)
Balanced ischemia on qualitative images
(C)
Evaluation of collateral flow
(D)
Identification of endothelial dysfunction
46.
Diffusely increased marrow FDG uptake may be secondary to all of the following EXCEPT:
(A)
Radiation therapy
(B)
Anemia
(C)
Inflammation
(D)
G-CSF therapy
47.
Malignant attributes of pulmonary nodules on computed tomography (CT) include:
(A)
Small size
(B)
Decrease in size over time
(C)
Round margins
(D)
Mixed attenuation
48.
PET has been shown to have reduced sensitivity in patients with colorectal:
(A)
Mucinous adenocarcinoma
(B)
Carcinoma in situ
(C)
Metastatic carcinoma
(D)
Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma
49.
According to the Cotswold system (formerly the Ann Arbor Staging System), involvement of a single lymph node region or involvement of a single extralymphatic organ outlines:
(A)
Stage I of lymphoma
(B)
Stage II of lymphoma
(C)
Stage III of lymphoma
(D)
Stage IV of lymphoma
50.
According to a facility’s protocol, the maximum F-18 FDG dose that could be injected to a patient is 14 mCi. A 12 mCi dose of F-18 FDG is calibrated for 8:00 a.m. If the patient comes an hour early, what is the earliest time the dose will be under 14 mCi?
(A)
7:45 am
(B)
7:30 am
(C)
7:15 am
(D)
7:00 am
51.
In rooms with a negative pressure, the direction of airflow at the boundaries of the room is:
(A)
Out of the room
(B)
Into the room
(C)
Around the room
(D)
Below the room
52.
Clinical semiology of seizures, one of the main areas of study in patients with epilepsy, evaluates:
(A)
Signs and symptoms
(B)
Electroencephalograms
(C)
Magnetoencephalograms
(D)
Autopsy findings
53.
Which of the following statements correctly explains the influence of FDG-PET imaging on staging in patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL)?
(A)
Upstaging of approximately 15–25% of patients
(B)
Downstaging in a small minority of patients
(C)
Upstaging in a small minority of patients
(D)
Downstaging of approximately 15–25% of patients
54.
A substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule and by binding to a site on a target protein serves as a signal triggering molecule is called:
(A)
Enzyme
(B)
Ligand
(C)
Tracer
(D)
Isotope
55.
Within the broad group of malignant lymphomas, the Hodgkin’s disease is set apart from other lymphomas by the presence of:
(A)
Splenomegaly
(B)
The Reed–Sternberg cells
(C)
The Schwann cells
(D)
Lymphadenopathy
56.
The brain structure described as a “sensory relay” is called:
(A)
The limbic system
(B)
The thalamus
(C)
The hypothalamus
(D)
The cerebellum
57.
A pencil shape, a fan shape, and a cone shape are commonly used terms in radiography to describe:
(A)
CT detector
(B)
PET crystal
(C)
X-ray beam
(D)
PET/CT fusion
58.
The tumors that arose from cells that stem from the neural crest cells, and share a characteristic feature to produce peptide hormones, as well as synthesize amines from certain precursors are called:
(A)
Sarcomas
(B)
Fibroid tumors
(C)
Adenocarcinomas
(D)
Neuroendocrine tumors
59.
All of the following statements appropriately describe the usefulness of FDG-PET imaging in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) EXCEPT:
(A)
FDG-PET reduces the number of futile surgical procedures
(B)
FDG-PET imaging is useful for guiding needle biopsy
(C)
FDG-PET/CT increases the accuracy of overall MPM staging
(D)
High levels of FDG uptake are associated with a favorable prognosis
60.
The radiation exposure rate at a distance of 12 inches from radioactive source is 12.5 mR/h. How many feet away should the technologist stand to reduce the exposure level to 3.0 mR/h?
(A)
2 ft
(B)
4.2 ft.
(C)
24.5 ft.
(D)
60 ft.
61.
The annual allowable limit for radiation exposure for the total effective dose equivalent (TEDE) to the whole body is less than or equal to:
(A)
10 mSv (1 rem)
(B)
20 mSv (2 rem)
(C)
50 mSv (5 rem)
(D)
500 mSv (50 rem)
62.
The amount of F-18 FDG uptake in atherosclerotic lesions correlates with:
(A)
The density of eosinophils in the lesions
(B)
The density of erythrocytes in the lesions
(C)
The density of macrophages in the lesions
(D)
The density of basophils in the lesions
63.
The attenuation-corrected (AC) PET, images when compared to the non-attenuation-corrected (NAC):
(A)
Have less noise
(B)
Require additional time
(C)
Are prone to artifacts
(D)
Don’t allow SUV measurement
64.
Selected tumors with low/variable FDG uptake include all of the following EXCEPT:
(A)
Bronchoalveolar carcinoma
(B)
Iodine-avid differentiated thyroid cancer
(C)
Metastatic liver carcinoma
(D)
Hepatocellular carcinoma
65.
Increased synthesis of monoclonal immunoglobulins in multiple myeloma functions as a straightforward approach for functional imaging with:
(A)
F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose
(B)
C-11 methionine
(C)
C-11 raclopride
(D)
F-18 fluoride
66.
When compared with Ga-68 DOTA-peptides, F-18DOPA may offer advantages for the detection of neuroendocrine tumors with:
(A)
A high expression of SSR
(B)
A low or absent expression of SSR
(C)
A decreased glucose metabolism
(D)
An increased glucose metabolism
67.
Cancer that starts in antibody producing white blood cells is called:
(A)
Lymphocytic leukemia
(B)
Multiple myeloma
(C)
Hodgkins lymphoma
(D)
Monocytic leukemia
68.
Hypometabolic area seen after radiation therapy in patients with treated CNS brain tumor, adjacent to or distant from the tumor is secondary to:
(A)
Inflammation
(B)
Edema
(C)
Stroke
(D)
Metastases
69.
The ECG records normal electrical currents as specific waves in the following order:
(A)
P wave, QRS complex, ST segment, T wave, and U wave
(B)
QRS complex, P wave, ST segment, T wave, and U wave
(C)
QRS complex, U wave, P wave, ST segment, and T wave
(D)
P wave, QRS complex, ST segment, U wave, and T wave
70.
The difference among the daily blank sinogram, and a reference blank sinogram acquired at some point in the last setup of the scanner, is called:
(A)
Average variance
(B)
Streak artifact
(C)
Scatter correction
(D)
Calibration factor
71.
Radiation dose equivalency is measured in:
(A)
Rad
(B)
Rem
(C)
Curie
(D)
Roentgen
72.
PET F-18 FDG findings commonly observed in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) include:
(A)
Diffusely increased F-18 FDG activity in the lungs
(B)
Decreased lung volume
(C)
Prominent right ventricle F-18 FDG uptake
(D)
Decreased anteroposterior thoracic diameter
73.
The main advantage of the Straton x-ray tube over the traditional x-ray tube results mainly from:
(A)
More effective shielding
(B)
More effective cooling and heat dissipation
(C)
Lower price and energy use
(D)
User-friendly interface
74.
All of the following statements correctly describe the postsurgical F-18 FDG uptake at the intervention site EXCEPT:
(A)
Postsurgical F-18 FDG uptake is mainly diffuse
(B)
Postsurgical F-18 FDG uptake corresponds to the site of surgery
(C)
Postsurgical F-18 FDG uptake increases in intensity with time
(D)
Postsurgical F-18 FDG uptake decreases in size with time
75.
The manifestation of hypermetabolic lesions in architecturally unchanged trabecular bone in patients with multiple myeloma suggests the presence of:
(A)
Scar tissue
(B)
Bone metastases
(C)
Active lesions
(D)
Avascular necrosis
76.
All of the following types of medications are affecting fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in patients with brain tumors EXCEPT:
(A)
Corticosteroids
(B)
Mineralocorticoids
(C)
Sedatives
(D)
Anticonvulsants
77.
The incremental prognostic value of PET myocardial perfusion imaging:
(A)
Predicts recovery time after cardiac events
(B)
Predicts time to hospital discharge
(C)
Predicts adverse cardiac events
(D)
Predicts cost of treatment
78.
The most common sites of neuroendocrine tumor (NET) onset are:
(A)
The bronchus/lungs and gastroenteropancreatic tract
(B)
The brain and the skin
(C)
The thyroid and urinary tract
(D)
Adrenal glands and genital tract
79.
All of the following findings have been observed on FDG-PET scans of patients with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) EXCEPT:
(A)
The higher focal activity was seen during disease exacerbation
(B)
The higher focal activity disappeared on the PET scan after antibiotic therapy
(C)
The PET foci showed corresponding CT scan findings
(D)
The higher focal activity disappeared on the CT scan after antibiotic therapy
80.
The following values were obtained from a Cs-137 measurement on a dose calibrator during a Monday to Friday workweek. What is the standard sample deviation of the series of measurements listed below?
490 μCi, 503 μCi, 482 μCi, 507 μCi, 514 μCi
(A)
499.2
(B)
675
(C)
168.7
(D)
13
81.
Ring dosimeters should be issued to individuals who are likely to exceed a minimum extremity dose of:
(A)
1,000 mrem/year (10 mSv/year)
(B)
2,000 mrem/year (20 mSv/year)
(C)
5,000 mrem/year (50 mSv/year)
(D)
10,000 mrem/year (100 mSv/year)
82.
Pattern of F-18 FDG uptake in the normal tonsils, soft palate, mylohyoid muscle, and sublingual glands observed on sagittal images is described as:
(A)
C shape
(B)
T shape
(C)
An inverted C shape
(D)
An inverted T shape
83.
The Society of Nuclear Medicine recommends that F-18 FDG-PET should be routinely performed on patients previously treated for differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) when the findings of radioactive iodine whole-body scintigraphy (WBS) are negative and:
(A)
The thyroglobulin (Tg) levels are more than 10 ng/mL
(B)
The thyroglobulin (Tg) levels are less than 10 ng/mL
(C)
The thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels are more than 30 mIU/L
(D)
The thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels are less than 30 mIU/L
84.
The following are amino acids EXCEPT:
(A)
Leucine
(B)
Methionine
(C)
Choline
(D)
Tyrosine
85.
A profile of the counts across the point source image is called:
(A)
System resolution
(B)
System sensitivity
(C)
Point spread function
(D)
Line spread function
86.
The most important single prognostic factor for survival and prognosis in patients diagnosed with neuroendocrine tumors is the presence of:
(A)
Brain metastasis
(B)
Lung metastasis
(C)
Liver metastasis
(D)
Lymph node metastasis
87.
The interaction between penetrating radiation and matter when the incident x-ray photon deflected from its original path loses energy but continues to travel through the material along an altered path is called:
(A)
The photoelectric effect
(B)
The Compton scattering
(C)
The pair production
(D)
Bremsstrahlung radiation
88.
Frontotemporal dementia is a clinical syndrome known as:
(A)
Pick’s disease
(B)
Vascular dementia
(C)
Alzheimer’s disease
(D)
Dementia with Lewy bodies
89.
All of the following positron emission tomography myocardial perfusion tracers are used for noninvasive myocardial blood flow (MBF) quantitation EXCEPT:
(A)
Water O-15
(B)
Rubidium Rb-82
(C)
Acetate C-11
(D)
Ammonia N-13
90.
91.
In the resting myocardium, and under normal conditions, 15% to 20% of the energy is delivered by:
(A)
Vitamin C
(B)
Glucose
(C)
Choline
(D)
Fatty acids
92.
Interictal PET scans are most valuable in the management of the patient with:
(A)
Partial complex seizures
(B)
Partial simple seizures
(C)
Petit mal seizures
(D)
Grand mal seizures
93.
PET/CT findings in anaplastic thyroid cancer scintigraphy can be described by all of the following EXCEPT:
(A)
PET and PET/CT define the local extent of disease and the presence of metastases
(B)
A positive PET/CT scan after therapy is linked with longer survival
(C)
PET and PET/CT have an impact on patients’ management
(D)
Intense FDG uptake and volume are prognostic for a bad outcome
94.
The FDG-PET sensitivity and specificity in restaging and follow-up of melanoma are accordingly:
(A)
56% and 45%
(B)
70% and 74%
(C)
92% and 94%
(D)
100% and 100%
95.
All of the following radiopharmaceuticals can be used for the evaluation of recurrent or residual medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) EXCEPT:
(A)
In-111 Octreoscan
(B)
C-11 acetate
(C)
F-18 DOPA
(D)
Ga-68 DOTATOC
96.
Possible explanations of relative insensitivity of FDG-PET for the detection of regional nodal metastases in patients with esophageal carcinoma include:
(A)
The mediastinal proximity
(B)
The primary tumor mass proximity
(C)
Esophagitis
(D)
Barrett esophagus
97.
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is the ratio obtained when the signal in an image is:
(A)
Divided by the background in the image
(B)
Multiplied by the background in the image
(C)
Divided by the noise in the image
(D)
Multiplied by the background in the image
98.
The following statements describing PET and PET/CT for the management of patients with breast cancer are true EXCEPT:
(A)
PET has limited sensitivity in detecting lesions less than 10 mm
(B)
PET/CT cannot detect a lesion beyond the resolution of CT
(C)
In situ carcinoma shows higher FDG uptake than invasive ductal cancer
(D)
Dense breast may mask small and low-grade tumors
99.
6-[F-18]fluoro-L-DOPA was developed as the PET tracer to visualize:
(A)
Neurons in the basal ganglia
(B)
Amyloid in the brain cortex
(C)
Viable myocardium
(D)
Sentinel node
100.
Which of the following structures function as the normal pacemaker of the heart?
(A)
Atrioventricular node
(B)
Sinoatrial node
(C)
Right bundle branches
(D)
Ventricular myocardium
101.
102.
The single most important factor in determining initial prognosis and the need for adjuvant chemotherapy for patients diagnosed with breast cancer is/are:
(A)
Axillary lymph node metastasis
(B)
Histologic tumor type
(C)
Tumor size
(D)
Mediastinal lymph node metastasis
103.
The primary difference between NEMA performance measurements, defined as NU 2-2007 and NU 2-2001, is:
(A)
NU 2-2007 addresses spatial resolution measurement using a point source
(B)
NU 2-2007 addresses the intrinsic radioactivity in LSO and LYSO crystals
(C)
NU 2-2001 addresses intrinsic scatter fraction measurement
(D)
NU 2-2001 addresses the intrinsic radioactivity in LSO and LYSO crystals
104.
The physiological breast uptake in postmenopausal women, who are NOT on hormone replacement therapy (HRT), should be:
(A)
Absent
(B)
Less than the liver
(C)
More than the liver
(D)
More than the heart
105.
All of the following factors contribute to degradation of resolution in the reconstructed images in positron emission tomography (PET) imaging EXCEPT:
(A)
Positron range
(B)
Inter-crystal scattering
(C)
The width of scintillation crystals
(D)
Photon collinearity
106.
In the evaluation of malignancy, misinterpreting normal uptake of F-18 FDG within the thymus results in a potential pitfall in the evaluation of the:
(A)
Posterior mediastinum
(B)
Anterior mediastinum
(C)
Pericardium
(D)
Pleura
107.
Scatter events comprise __________ in 3D positron emission tomography (PET):
(A)
10–20% of all events
(B)
20–30% of all events
(C)
30–40% of all events
(D)
40–60% of all events
108.
F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) use in patients with suspected primary and residual/recurrent gliomas is limited by:
(A)
The low F-18 FDG uptake in normal brain tissue
(B)
The high F-18 FDG uptake in normal brain tissue
(C)
The low F-18 FDG uptake in tumor tissue
(D)
The high F-18 FDG uptake in tumor tissue
109.
The most important problem with the PET/MR scanner is:
(A)
Correcting for attenuation of gamma rays
(B)
Correcting for scatter of gamma rays
(C)
Correcting for patient motion
(D)
Correcting for breathing artifacts
110.
The path distance required for a positron to find an electron for annihilation depends on:
(A)
The number of positrons and number of electrons in the immediate area of decay
(B)
The energy of positron and number of electrons in the immediate area of decay
(C)
The energy of positron and energy of electron in the immediate area of decay
(D)
The number of positrons and charge of electron in the immediate area of decay
111.




Abnormal bone FDG uptake by tumor cells is proportional to:
(A)
Blood flow
(B)
Osteoblastic activity
(C)
Glucose metabolism
(D)
Cell wall synthesis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree