and Adam Sciuk2
(1)
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Resurrection Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA
(2)
Department of Radiology, Resurrection Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA
Abstract
Answers to Test #4 begin on page 240.
Questions
1.
What enzyme traps FDG inside the cell?
(A)
Glucoso-6-phosphatase
(B)
Hexokinase
(C)
Isomerase
(D)
GLUT-1
2.
The standard uptake value (SUV) is:
(A)
The measured activity divided by the body mass
(B)
The amount of tracer needed for a particular body weight
(C)
The measured activity normalized for body weight/surface area and injected dose
(D)
The measured activity within a particular organ divided by the sampled volume
3.
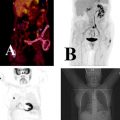
What should have been done to avoid the artifact illustrated in Fig. 5.1?
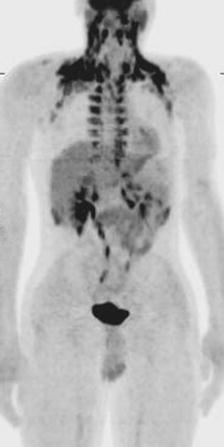

Fig. 5.1
PET/CT MIP image
(A)
Administer insulin
(B)
Administer glucose
(C)
Keeping the patient warm during the uptake phase after the FDG injection
(D)
Keeping the patient cool during the uptake phase after the FDG injection
4.
The most common site of distant metastases in non-small cell lung cancer the most common distant metastasis is:
(A)
The liver
(B)
The spleen
(C)
The adrenal glands
(D)
The kidneys
5.
The radiation absorbed dose (rad) of 350 is equal to how many grays (Gy)?
(A)
350,000 Gy
(B)
35,000 Gy
(C)
3.5 Gy
(D)
0.350 Gy
6.
How can a patient’s radiation exposure be minimized during FDG-PET imaging?
(A)
Shorter imaging time
(B)
Collimation
(C)
Using lead shields
(D)
Decreasing the administered FDG dose
7.
The most common gastric cancer worldwide is:
(A)
Adenocarcinoma
(B)
Lymphoma
(C)
Leiomyosarcoma
(D)
Squamous cell carcinoma
8.
The presented PET MIP image in Fig. 5.2 was obtained in routine PET/CT examination. Which of the following expressions can be found in the body of the radiologist’s report describing the exam’s findings?
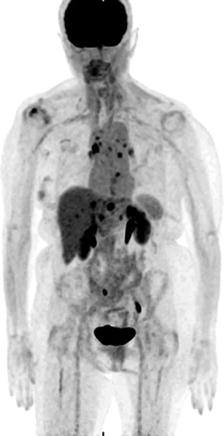

Fig. 5.2
PET/CT MIP image
(A)
Hypermetabolic activity in the infracarinal region…increased activity in both adrenal glands…
(B)
Mass at the right lung base with rim of increased activity…increased activity in the left adrenal…
(C)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci….liver metastases
(D)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci…physiologic uptake in the abdomen and pelvis
9.
The principal criteria by computed tomography (CT) for defining the presence of nodal metastases is:
(A)
Size
(B)
Shape
(C)
Metabolic activity
(D)
Presence of calcifications
10.
An unshielded F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose dose is producing an exposure rate of 25 mR/h. How many HVLs of lead must be used to reduce the exposure rate to 1.5 mR/h? The half value layer of F-18 is 4.1 mm of lea(D)
(A)
16.6 mm
(B)
4 HVLs
(C)
16.6 HVLs
(D)
4 mm
11.
FDG-PET imaging is not indicated for initial staging in what type of malignancy?
(A)
Breast cancer
(B)
Hodgkin’s lymphoma
(C)
Prostate cancer
(D)
Lung cancer
12.
The presented PET MIP image in Fig. 5.3 was obtained in routine PET/CT examination. Which of the following expressions can be found in the body of the radiologist’s report describing the exam’s findings?
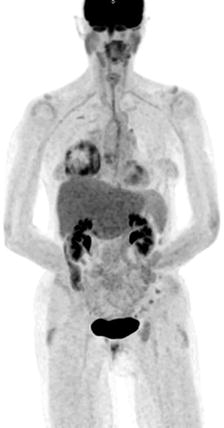

Fig. 5.3
PET/CT MIP image
(A)
Hypermetabolic activity in the infracarinal region…increased activity in both adrenal glands…
(B)
Mass at the right lung base with rim of increased activity…physiologic uptake in the bladder…
(C)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci….liver metastases
(D)
The chest demonstrates several punctate hypermetabolic foci…physiologic uptake in the abdomen and pelvis
13.
The best FDG-PET results in epilepsy diagnosis have been obtained in what kind of condition?
(A)
Epilepsy occurring secondary to brain tumor
(B)
Epilepsy occurring secondary to arrest of neuronal migration
(C)
Epilepsy occurring secondary to mesial temporal sclerosis
(D)
Epilepsy occurring secondary to generalized brain atrophy
14.
Convert 13,920 microcuries (μCi) to Curies (Ci).
(A)
0.001392 Ci
(B)
0.01392 Ci
(C)
1392 Ci
(D)
13920 Ci
15.
What is the 5-year survival rate for a lung cancer patient with a Stage I disease?
(A)
71%
(B)
61%
(C)
51%
(D)
41%
16.
The most common esophageal cancer worldwide is:
(A)
Squamous cell carcinoma
(B)
Adenocarcinoma
(C)
Sarcoma
(D)
Oat cell carcinoma
17.
A PET imaging agent for Alzheimer’s disease that gained FDA approval in 2012 is called:
(A)
Amiloride
(B)
Amyloid
(C)
Amyvid
(D)
Ambien
18.
The pattern of myocardial blood flow combined with myocardial glucose metabolism in dysfunctional, but viable myocardium, is described as:
(A)
Decreased myocardial blood and decreased myocardial glucose metabolism
(B)
Decreased myocardial blood and retained myocardial glucose metabolism
(C)
Normal myocardial blood and decreased myocardial glucose metabolism
(D)
Normal myocardial blood and retained myocardial glucose metabolism
19.
In the process of interpretation and analysis of PET/CT images, a study demonstrating a focal localized disease process, which could not be confirmed as being the cause of the fever of unknown origin (FUO) or malignancy, is called:
(A)
False positive
(B)
False negative
(C)
True negative
(D)
True positive
20.
The pattern of FDG uptake/glucose metabolism in patients with Alzheimer disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of:
(A)
Frontal hypometabolism
(B)
Scattered foci of hypometabolism
(C)
Occipital hypometabolism
(D)
Parietotemporal hypometabolism
21.
Excessive F-18 FDG metabolic activity in the thoracic expiratory musculature in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is observed in:
(A)
The deltoid muscles
(B)
The sternocleidomastoid muscles
(C)
The trapezius muscles
(D)
The intercostal muscles
22.
A Cancer facility has a protocol that implements a 14 mCi dose as the maximum activity limit of F-18 FDG that could be injected into patients. A dose of F-18 FDG is calibrated to have 14 mCi/2 ml at 16:00 h. If the patient shows up an hour early at 15:00 h for their appointment, what activity should be subtracted to make it 14 mCi at 15:00 h?
(A)
0.6 ml
(B)
1.4 ml
(C)
6.4 mCi
(D)
9.6 mCi
23.
A rise in which of the following markers is suggestive of thyroid cancer recurrence in patients that have had a total thyroidectomy?
(A)
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
(B)
Tg (thyroglobulin)
(C)
T4 (thyroxin)
(D)
TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone)
24.
Esophageal malignancy associated with Barrett’s esophagus is:
(A)
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
(B)
Adenocarcinoma
(C)
Sarcoma
(D)
Oat cell carcinoma
25.
What is the reason for the uptake pattern illustrated in Fig. 5.4?
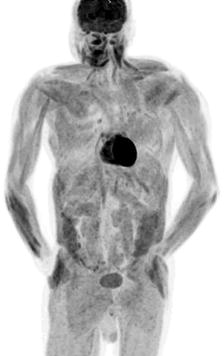

Fig. 5.4
PET MIP image
(A)
Starvation
(B)
Hypoglycemia
(C)
Non-fasting state
(D)
High injected FDG dose
26.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

How many microcuries (μCi) is 5.7 megabecquerels (MBq)?
(A)
153,900 μCi
(B)
153.9 μCi
(C)
21.09 μCi