| Skull Base Region | Left sella turcica and left cavernous sinus |
| Histopathology | N/A |
| Prior Surgical Resection | Yes |
| Pertinent Laboratory Findings | Prolactin: 200 ng/mL |
Case description
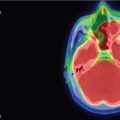
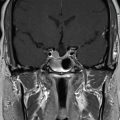
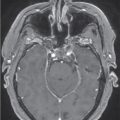
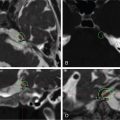
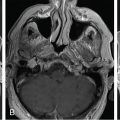
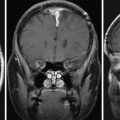
A 35-year-old female with a 3-month history of amenorrhea was found to have prolactin levels elevated to 200 ng/mL. Imaging revealed a left-sided pituitary microadenoma ( Figure 3.15.1 ). She was started on cabergoline 0.25 mg twice a week, and her prolactin subsequently dropped to 140 ng/mL. Her cabergoline regimen was increased to three times weekly, but this dose did not result in normal prolactin levels. Imaging obtained a year later showed interval growth of the tumor along the left side of the sella turcica, contiguous with the wall of the left cavernous sinus. She was diagnosed with a medically resistant prolactinoma and was referred for surgical excision via a sublabial microscopic transsphenoidal approach. The sellar portion of the tumor was fully excised, although the lateral aspect was found to have likely dural invasion, and residual tumor was left within the left cavernous sinus ( Figure 3.15.2 ). Postoperatively, her prolactin levels dropped to 70.5 ng/mL but were still elevated, so she was referred for stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) ( Figure 3.15.3 ).
| Radiosurgery Machine | Gamma knife |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) | 25, at 50% isodose line |
| Number of Fractions | 1 |



| Critical Structure | Dose Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Optic nerve/chiasm |
|
| Brainstem |
|
| Cranial nerves in cavernous sinus |
|
| Cavernous carotid artery |
|
| Normal pituitary gland and pituitary stalk | Recommend to limit radiation exposure to the identifiable gland to <11.0 Gy and to avoid whole-sella SRS whenever possible |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree