Pulmonary Arteries
Melissa L. Rosado-de-Christenson, MD, FACR
Gerald F. Abbott, MD
Terminology
Abbreviations
Secondary pulmonary lobule (SPL)
Overview of Pulmonary Arteries
Morphology
Branching tapering tubular structures
Terminate in capillary network of alveolar walls
Bronchoarterial bundle
Pulmonary arteries
Airways
Function
Conduit of deoxygenated blood from right heart to capillary-alveolar interface
Collateral blood flow via vascular anastomoses with bronchial arteries
Anatomy of Pulmonary Arteries
General Concepts
Right ventricle gives rise to pulmonary trunk
Pulmonary trunk gives rise to right and left pulmonary arteries
Pulmonary artery branches
Lobar
Segmental
Subsegmental
Histology
Proximal large pulmonary arteries → elastic arteries
Distal small pulmonary arteries → transition to muscular arteries at level of bronchiole
Smallest pulmonary arteries → loss of smooth muscle in vessel wall
Imaging of Normal Arteries
Imaging Anatomy
Central pulmonary arteries course and branch alongside bronchi
Medial to bronchi in upper lobes
Lateral to bronchi in middle lobe, lingula, and lower lobes
Peripheral pulmonary arteries course along bronchioles
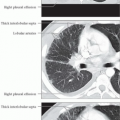
Lobular artery of SPL
Central or centrilobular location in SPL
Measures approximately 1 mm in diameter
Lobular core; central portion of SPL containing pulmonary artery and adjacent bronchiole
Imaging Features
Central pulmonary arteries
Rounded or ovoid opacities when imaged perpendicular to their long axis
Tubular tapering opacities when imaged along their long axis
Parallel course of accompanying bronchi
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree