Pyloric Stenosis
Parth C. Patel
Cassandra M. Sams
CLINICAL HISTORY
6-week-old male who presented with projectile, nonbloody, and nonbilious vomiting after every feed for 4 days.
FINDINGS
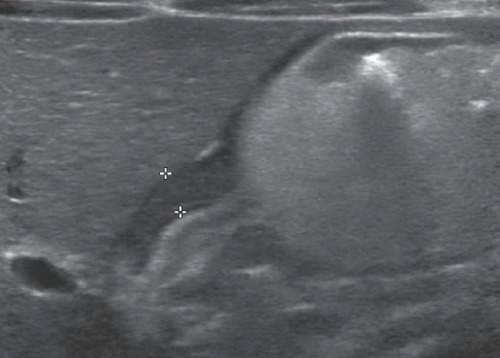
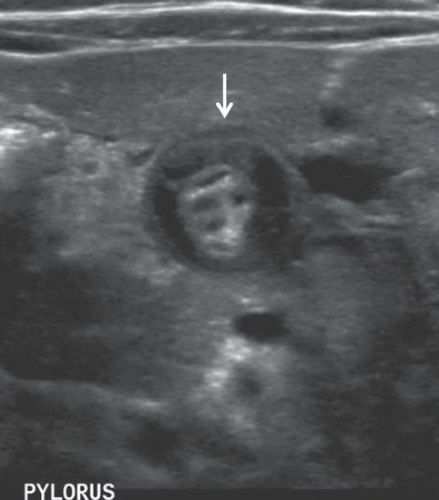
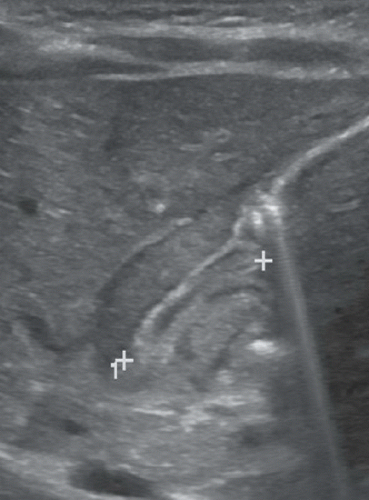
Figure 91A: Longitudinal ultrasound image of the pylorus demonstrates a thickened pyloric muscle measuring 4.1 mm (between cursors). Figure 91B: Longitudinal ultrasound image of the pylorus shows a markedly thickened, hypoechoic gastric pyloric muscle with an elongated pyloric canal length measuring 17 mm (between cursors). Figure 91C: Transverse US image of the pyloric channel shows the target sign of pyloric stenosis (arrow) because of circumferential hypertrophied hypoechoic muscle surrounding echogenic mucosa.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pylorospasm, gastroesophageal reflux, midgut volvulus, duodenal web/stenosis, annular pancreas, and hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.