Chapter 7 Recognizing Pneumonia
General Considerations
 Pneumonia can be defined as consolidation of lung produced by inflammatory exudate, usually as a result of an infectious agent.
Pneumonia can be defined as consolidation of lung produced by inflammatory exudate, usually as a result of an infectious agent. Other pneumonias demonstrate interstitial disease, and others produce findings in both the airspaces and the interstitium.
Other pneumonias demonstrate interstitial disease, and others produce findings in both the airspaces and the interstitium. Most microorganisms that produce pneumonia are spread to the lungs via the tracheobronchial tree, either through inhalation or aspiration of the organisms.
Most microorganisms that produce pneumonia are spread to the lungs via the tracheobronchial tree, either through inhalation or aspiration of the organisms. In some instances, microorganisms are spread via the bloodstream and in even fewer cases, by direct extension.
In some instances, microorganisms are spread via the bloodstream and in even fewer cases, by direct extension. Because many different microorganisms can produce similar imaging findings in the lungs, it is difficult to identify with certainty the causative organism from the radiographic presentation alone.
Because many different microorganisms can produce similar imaging findings in the lungs, it is difficult to identify with certainty the causative organism from the radiographic presentation alone.• However, certain patterns of disease are very suggestive of a particular causative organism (Table 7-1).
TABLE 7-1 PATTERNS THAT MIGHT SUGGEST A CAUSATIVE ORGANISM
| Pattern of Disease | Likely Causative Organism |
|---|---|
| Upper lobe cavitary pneumonia with spread to the opposite lower lobe | Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) |
| Upper lobe lobar pneumonia with bulging interlobar fissure | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Lower lobe cavitary pneumonia | Pseudomonas aeruginosa or anaerobic organisms (Bacteroides) |
| Perihilar interstitial disease or perihilar airspace disease | Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) |
| Thin-walled upper lobe cavity | Coccidioides (Coccidiomycosis), TB |
| Airspace disease with effusion | Streptococci, staphylococci, TB |
| Diffuse nodules | Histoplasma, Coccidioides, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (histoplasmosis, coccidiomycosis, TB) |
| Soft-tissue, fingerlike shadows in upper lobes | Aspergillus (allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis) |
| Solitary pulmonary nodule | Cryptococcus (cryptococcosis) |
| Spherical soft-tissue mass in a thin-walled upper lobe cavity | Aspergillus (aspergilloma) |
General Characteristics of Pneumonia
• Because pneumonia fills the involved airspaces or interstitial tissues with some form of fluid or inflammatory exudate, pneumonias appear denser (whiter) than the surrounding, normally aerated lung.
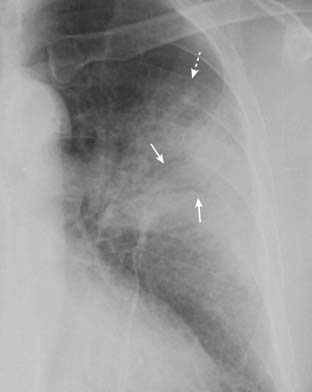
• Pneumonia may contain air bronchograms if the bronchi themselves are not filled with inflammatory exudate or fluid (see Fig. 3-3).
• Air bronchograms are much more likely to be visible when the pneumonia involves the central portion of the lung near the hilum. Near the periphery of the lung, the bronchi are usually too small to be visible (Fig. 7-1).
 Interstitial pneumonia, on the other hand, may produce prominence of the interstitial markings in the affected part of the lung or may spread to adjacent airways and resemble airspace disease.
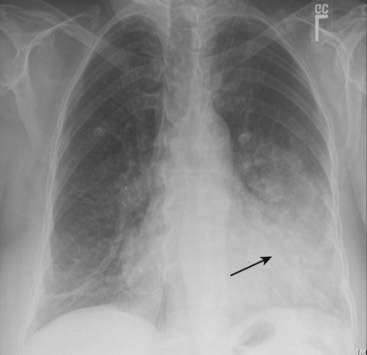
Interstitial pneumonia, on the other hand, may produce prominence of the interstitial markings in the affected part of the lung or may spread to adjacent airways and resemble airspace disease. Except for the presence of air bronchograms, airspace pneumonia is usually homogeneous in density (Fig. 7-2).
Except for the presence of air bronchograms, airspace pneumonia is usually homogeneous in density (Fig. 7-2). In some types of pneumonia (i.e., bronchopneumonia), the bronchi, as well as the airspaces, contain inflammatory exudate. This can lead to atelectasis associated with the pneumonia.
In some types of pneumonia (i.e., bronchopneumonia), the bronchi, as well as the airspaces, contain inflammatory exudate. This can lead to atelectasis associated with the pneumonia.Box 7-1 Recognizing a Pneumonia—Key Signs
In airspace disease, the margins may be fluffy and indistinct except where they abut a pleural surface like the interlobar fissures where the margin will be sharp.
Interstitial pneumonias will cause a prominence of the interstitial tissues of the lung in the affected area; in some cases, the disease can spread to the alveoli and resemble airspace disease.
Patterns of Pneumonia
 Pneumonias may be distributed in the lung in several patterns described as lobar, segmental, interstitial, round, and cavitary (Table 7-2).
Pneumonias may be distributed in the lung in several patterns described as lobar, segmental, interstitial, round, and cavitary (Table 7-2). Remember, these are terms that simply describe the distribution of the disease in the lungs; they aren’t diagnostic of pneumonia because many other diseases can produce the same patterns of disease distribution in the lung.
Remember, these are terms that simply describe the distribution of the disease in the lungs; they aren’t diagnostic of pneumonia because many other diseases can produce the same patterns of disease distribution in the lung.TABLE 7-2 PATTERNS OF APPEARANCE OF PNEUMONIAS
| Pattern | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Lobar | Homogeneous consolidation of affected lobe with air bronchogram |
| Segmental (bronchopneumonia) | Patchy airspace disease frequently involving several segments simultaneously; no air bronchogram; atelectasis may be associated |
| Interstitial | Reticular interstitial disease usually diffusely spread throughout the lungs early in the disease process; frequently progresses to airspace disease |
| Round | Spherically shaped pneumonia usually seen in the lower lobes of children that may resemble a mass |
| Cavitary | Produced by numerous microorganisms, chief among them being Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
Lobar Pneumonia
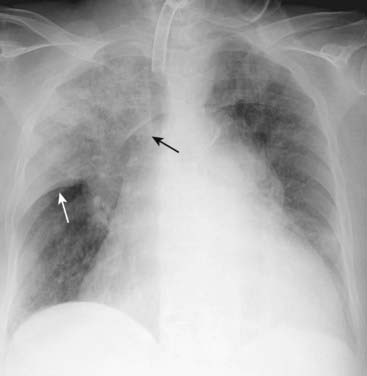
 The prototypical lobar pneumonia is pneumococcal pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (Fig. 7-3).
The prototypical lobar pneumonia is pneumococcal pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (Fig. 7-3). Although we are calling it lobar pneumonia, the patient may present before the disease involves the entire lobe. In its most classic form, the disease fills most or all of a lobe of the lung.
Although we are calling it lobar pneumonia, the patient may present before the disease involves the entire lobe. In its most classic form, the disease fills most or all of a lobe of the lung. Because lobes are bound by interlobar fissures, one or more of the margins of a lobar pneumonia may be sharply marginated.
Because lobes are bound by interlobar fissures, one or more of the margins of a lobar pneumonia may be sharply marginated. Lobar pneumonias almost always produce a silhouette sign where they come in contact with the heart, aorta, or diaphragm, and they almost always contain air bronchograms if they involve the central portions of the lung.
Lobar pneumonias almost always produce a silhouette sign where they come in contact with the heart, aorta, or diaphragm, and they almost always contain air bronchograms if they involve the central portions of the lung.Segmental Pneumonia (Bronchopneumonia)
 The prototypical bronchopneumonia is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Many gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can produce the same picture.
The prototypical bronchopneumonia is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Many gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can produce the same picture. Brochopneumonias are spread centrifugally via the tracheobronchial tree to many foci in the lung at the same time. Therefore they frequently involve several segments of the lung simultaneously.
Brochopneumonias are spread centrifugally via the tracheobronchial tree to many foci in the lung at the same time. Therefore they frequently involve several segments of the lung simultaneously. Because lung segments are not bound by fissures, all of the margins of segmental pneumonias tend to be fluffy and indistinct (Fig. 7-4).
Because lung segments are not bound by fissures, all of the margins of segmental pneumonias tend to be fluffy and indistinct (Fig. 7-4).