KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Recurrent episodes of acute pyogenic cholangitis with intra- and extrahepatic biliary pigment stones
- •
Synonyms: Hepatolithiasis, oriental cholangiohepatitis
Imaging
- •
Intra- and extrahepatic biliary ductal dilatations with stones
- •
Lateral segment of left lobe and posterior segment of right lobe more commonly involved
- •
Biliary ductal thickening due to repeated inflammation
- •
Severe atrophy of affected lobe/segment, biliary cirrhosis
- •
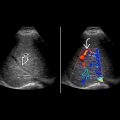
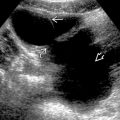
Grayscale ultrasound
- ○
Presence of echogenic sludge/stones ± posterior acoustic shadowing in intrahepatic and extrahepatic duct
- ○
Periportal hypo-/hyperechogenicity due to periductal inflammation
- ○
Ductal rigidity and straightening, rapid tapering of peripheral intrahepatic duct
- ○
- •
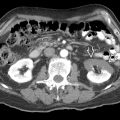
Cholangiography and MRCP
- ○
Intra- and extrahepatic duct dilatation with stones as filling defects
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Ascending cholangitis
- •
Sclerosing cholangitis
- •
Cholangiocarcinoma
- •
Intrahepatic stones secondary to biliary stricture
- •
Caroli disease
Clinical Issues
- •
Common symptoms/signs: Recurrent episodes of RUQ pain, fever, and jaundice
- •
Risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma (5-6%)
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Consider recurrent pyogenic cholangitis in southeast Asian patients with recurrent episodes of acute bacterial cholangitis
- •
Imaging interpretation pearl: Intra- and extrahepatic bile duct dilatation with pigmented stones and ductal inflammation
Scanning Tips
- •
To better demonstrate posterior acoustic shadowing of intrahepatic stones, consider turning off compounding
- •
Echogenic sludge may be mistaken for artifact; zooming in or changing windows may help to distinguish real echoes from artifact
 and extrahepatic
and extrahepatic  bile ducts with multiple common bile duct and intrahepatic duct stones. The peripheral intrahepatic duct shows rapid tapering and decreased arborization.
bile ducts with multiple common bile duct and intrahepatic duct stones. The peripheral intrahepatic duct shows rapid tapering and decreased arborization.
 with posterior acoustic shadowing
with posterior acoustic shadowing  in the right hepatic duct causing upstream intrahepatic bile duct dilatation
in the right hepatic duct causing upstream intrahepatic bile duct dilatation  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree