KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Purulent &/or necrotic intraparenchymal or perinephric collection arising from unresolved pyelonephritis
Imaging
- •
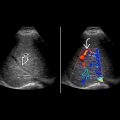
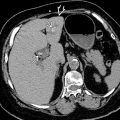
Complex cystic mass, may be sharply marginated or more permeative
- •
Rim may be hypervascular, or vessels may course to edge of lesion and stop
- •
Findings of pyelonephritis (renal enlargement, lack of corticomedullary differentiation, and urothelial thickening) may be present
- •
Internal echogenic foci with “comet tail” may represent gas-forming organisms within abscess
Pathology
- •
Ascending urinary tract infections (80%)
- ○
Corticomedullary abscess by Escherichia coli or Proteus species
- ○
- •
Hematogenous spread (20%)
- ○
Cortical abscess by Staphylococcus aureus
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
Abscess emerges after 10-14 days of untreated or undertreated urinary tract infection, not on 1st day of symptoms
- •
Antibiotic therapy, usually IV ± percutaneous drainage
- •
Surgical drainage or nephrectomy are rarely needed
Scanning Tips
- •
Many abscesses appear mass-like and may mimic neoplasms; careful evaluation with color Doppler may show minimal internal vascularity
- •
Look for surrounding echogenic fat, which indicates associated inflammatory changes
- •
Because findings can be subtle, change scanning windows and alter phase of respiration while scanning to help attain best image