KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
Usually small and round, may be wedge-shaped
- •
Usually cortical; rarely disrupting renal contour or capsule
- ○
Large, exophytic metastases may be encountered
- ○
- •
Hypoechoic, hyperechoic, or sonographically occult
- •
Occasionally infiltrative
- •
Perinephric infiltration from tumor extension or hemorrhage may be seen (melanoma)
- •
Mostly avascular or hypovascular using low-flow Doppler settings
- •
Melanoma (and other hypervascular primary tumors) metastasis can be hypervascular, simulating renal carcinoma
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Primary renal malignancy
- •
Renal angiomyolipoma
- •
Renal cysts (complex)
- •
Renal lymphoma or leukemia
- •
Renal infection
- •
Renal infarction
Clinical Issues
- •
May have hematuria or microhematuria (12-31%)
- •
Most are clinically occult and found on imaging or at autopsy
- •
Most common malignant renal tumor at autopsy (7-13% of autopsies); 20% of patients dying of disseminated malignancy
- •
Most patients have metastatic tumor at other locations
- •
Lung cancer most common primary site followed by breast, gastric cancer, melanoma, and lymphoma
- •
Prognosis very poor
Scanning Tips
- •
Metastases may be subtle on ultrasound; use color Doppler at low-flow settings
- •
Presence of disseminated malignancy suggests metastases as cause of abnormal renal ultrasound
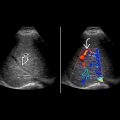
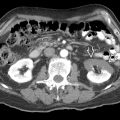
 representing metastatic melanoma. This cannot be distinguished from renal cell carcinoma.
representing metastatic melanoma. This cannot be distinguished from renal cell carcinoma.
 . While the grayscale features are indistinguishable from renal cell carcinoma, metastases are typically hypovascular compared to renal cell carcinoma.
. While the grayscale features are indistinguishable from renal cell carcinoma, metastases are typically hypovascular compared to renal cell carcinoma.