KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Contained rupture secondary to defect in artery wall
Imaging
- •
Usually in renal parenchyma, rarely extrarenal
- •
Usually ≤ 1 cm
- •
Extrarenal pseudoaneurysm may be larger
- •
Saccular, round or ovoid lesion
- •
Mimics simple or complex renal cyst on grayscale but with pulsations or swirling internal echoes
- •
Doppler: High-velocity jet into sac with internal turbulent flow
- ○
Swirling yin-yang internal flow
- ○
To-and-fro waveform in neck
- ○
- •
Internal clot when large
- •
CTA/MRA are confirmatory tests, which provide additional information about entire arterial tree
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Cyst
- •
Arteriovenous fistula, may coexist with pseudoaneurysm
- •
Perinephric collection (extra renal pseudoaneurysm)
Pathology
- •
Intrarenal: Iatrogenic injury during biopsy or percutaneous procedure
Clinical Issues
- •
Most asymptomatic
- •
Hematuria, abnormal renal function
- •
Pain, bleeding/hypotension from rupture
- •
Increased risk of rupture when extrarenal and > 2 cm
Scanning Tips
- •
Always turn on color Doppler when evaluating renal cystic lesions
- •
Look for characteristic to-and-fro flow in neck
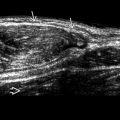
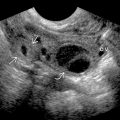
 in the lower pole of a renal transplant. Yin-yang internal swirling flow is present. Color aliasing is noted in the feeding artery
in the lower pole of a renal transplant. Yin-yang internal swirling flow is present. Color aliasing is noted in the feeding artery  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree