KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
No specific imaging characteristics
- •
Ultrasound-guided renal biopsy is gold standard
- •
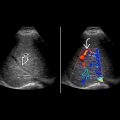
Acute rejection (AR): Nonspecific allograft edema, urothelial thickening
- •
Resistive index (RI) may be elevated, or there may be loss or reversal of arterial diastolic flow
- •
Elevated RI > 0.80 in early postoperative period associated with increased risk of graft failure
- •
Chronic rejection (CR): Cortical atrophy, increased echogenicity, calcification
- •
Color perfusion may be decreased in both AR or CR
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Acute tubular necrosis/delayed graft function
- •
Infection
- •
Renal vascular thrombosis
- •
Calcineurin inhibitor toxicity
Pathology
- •
AR and CR: Diagnosed and staged pathologically
Clinical Issues
- •
14% in first 3-6 months
- •
Acute cellular rejection most common after postoperative day 4
- •
Symptoms and signs include elevation of creatinine, decreased urine output, fever, graft tenderness and swelling
Scanning Tips
- •
Interval graft enlargement and tenderness with normal perfusion are suggestive of AR
- •
Poor correlation between RI and rejection
- ○
Small, hypoperfused, hyperechoic renal transplants are compatible with CR
- ○
 are less conspicuous.
are less conspicuous.