Chapter 6 Right ventricle
Right ventricular structure and function
Right ventricle
The right ventricle (RV) has gained more interest in recent decades following recognition of its significance in heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease, and complications of cardiac surgery. However, despite advances in cardiovascular imaging, the RV still causes significant challenges for most of the imaging modalities. Its complex shape and orientation makes it difficult to evaluate using 2D cross-sectional imaging modalities such as 2D echocardiography or radionuclide ventriculography.
Anatomy
The right ventricle lies anteriorly to the left ventricle, and is a complex cavity, more triangular or crescent-shaped than ellipsoid, with thin muscular walls (Fig. 6.1). This distinctive structure allows its anatomical differentiation from the left ventricle, which is especially helpful in diagnosing congenital heart diseases.
Morphological features of the right ventricle
 Presence of a moderator band
Presence of a moderator band
 Coarse trabeculation
Coarse trabeculation
 Three or more papillary muscles
Three or more papillary muscles
 Trileaflet configuration of the atrioventricular valve
Trileaflet configuration of the atrioventricular valve
 Septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve more apical than the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve.
Septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve more apical than the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve.
Cardiovascular imaging
The right ventricle presents several challenges for imaging. Echocardiography is the first-line investigation of the right ventricle but for precise measures of size and myocardial structure further imaging with cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) may be required. The reasons for the complexities in imaging the right ventricle are as follows.
 Complex geometry. Currently, there is no universal model for RV geometry, mostly because of its complex shape. This often leads to inaccuracies in volume measurements and a significant variability in measurements obtained with different imaging modalities.
Complex geometry. Currently, there is no universal model for RV geometry, mostly because of its complex shape. This often leads to inaccuracies in volume measurements and a significant variability in measurements obtained with different imaging modalities.
 Complex contraction pattern.
Complex contraction pattern.
 Heavily trabeculated thin myocardium.
Heavily trabeculated thin myocardium.
 Several rapidly changing indices of its function.
Several rapidly changing indices of its function.
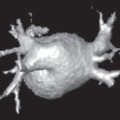
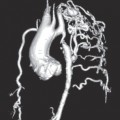
Fig. 6.1 Commercial analysis packages are now able to post-process 3D imaging data files, in particular echocardiographic files, to generate 3D volume reconstructions and functional analysis. In this image, TomTec has been used to generate a 3D volume of the right ventricle.
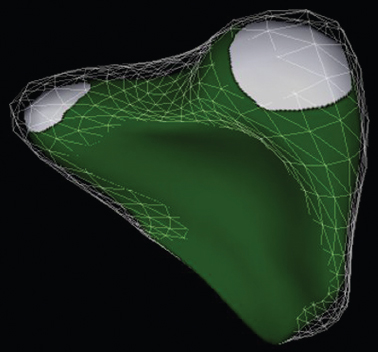
Right ventricular structure and function
Right ventricular shape and size
The complex shape of the right ventricle creates challenges for geometric modelling in imaging (Fig. 6.2). It also depends significantly on current physiological parameters, and can dynamically adjust to changes in pressure and/or volume. In addition, it is influenced by changes in the left ventricular structure.
Right ventricular function
The right ventricle has approximately one-sixth of the muscle mass and performs against one-tenth of the vascular resistance compared with the left ventricle. Right ventricle systolic function depends on:
 preload
preload
 intravascular volume
intravascular volume
 right ventricle compliance
right ventricle compliance
 heart rate
heart rate
 right atrial function
right atrial function
 pericardial function
pericardial function
 right ventricular contractility
right ventricular contractility
 afterload
afterload
 pulmonary resistance
pulmonary resistance
 left ventricular filling.
left ventricular filling.
Right ventricular myocardial blood supply
The right ventricle is supplied mostly by the right coronary artery in the prevalent right-dominant system. A smaller area, mostly in the anteroseptal region, is supplied by the left anterior descending artery.
Ventricular interdependence
As the right ventricle has thinner walls and lower pressure than the left ventricle, it depends strongly on left ventricular function, specifically on interventricular septal changes. In contrast, in the case of significant right ventricular dilatation and a corresponding shift of the interventricular septum to the left, left ventricular function will be influenced by right ventricular function.
Fig. 6.2 The variable anatomy of the right ventricle means that guidelines have been developed based on multiple measurements of right ventricular size in standardized locations. The figure shows these key measurements of length and width.
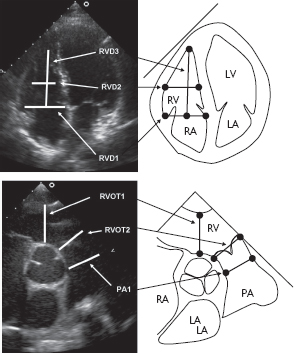
Echocardiography
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree