SCCa, Unknown Primary Site
Deborah R. Shatzkes, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
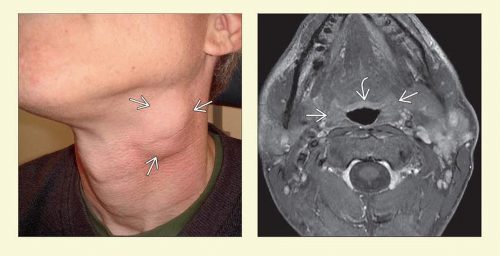
SCCa in cervical lymph node with clinically occult primary site
Carcinoma of unknown primary (CUP)
Imaging
CECT or MR first-line imaging tool
PET/CT may be helpful if this imaging negative
If primary site discovered, most often tonsil, tongue base, nasopharynx, or pyriform sinus apex
Cystic lymph nodes → think oropharynx
Primary tumor may be predicted from site of nodes
Parotid nodes from periauricular/facial skin SCCa
Posterior triangle nodes from scalp SCCa
Supraclavicular nodes from chest or abdomen SCCa
Top Differential Diagnoses
2nd branchial cleft cyst
Nodal differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Pathology
Nodal tissue tested for HPV/p16 and EBV markers, suggesting oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal tumor, respectively
Clinical Issues
Neck mass → FNA yields SCCa → office exam negative → imaging → panendoscopy + directed biopsies
Identification of primary tumor site can reduce morbidity and mortality by allowing targeted radiation therapy
Diagnostic Checklist
Understanding nodal drainage pathways helps direct interrogation for primary site
View asymmetry in most common primary sites with extreme suspicion
HPV/p16(+) &/or cystic nodes suggests oropharynx!
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Carcinoma of unknown primary (CUP)
Primary unknown cervical lymph node metastasis (PUCLNM)
Definitions
SCCa in cervical lymph node with unknown primary site after clinical examination
IMAGING
General Features
Location
If primary site is discovered, most often tonsil, tongue base, nasopharynx, pyriform sinus apex
Deep palatine and lingual tonsillar crypts may harbor small foci of SCCa
Fossa of Rosenmüller (nasopharynx) & pyriform sinus apex (hypopharynx) difficult to assess by office exam
Location of primary can sometimes be predicted from site of adenopathy
Parotid nodes from periauricular/facial skin SCCa
Skin primaries may have been previously resected, and neither clinically evident nor reported in patient history
Suboccipital nodes from scalp SCCa
Isolated supraclavicular node (“Virchow node”) from infraclavicular primary
Chest, breast, or abdominal/pelvic primary site
More common on left when primary is abdominal/pelvic
CT Findings
CECT
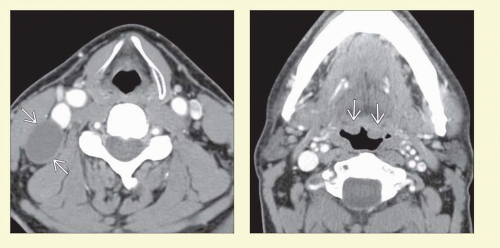
Solid or cystic nodal metastasis in neck
Most often found at level II
Must search for subtle fullness, increased enhancement, or asymmetry of pharyngeal mucosa
MR Findings
Primary tumor in depths of tonsil may be more readily evident on MR than CECT
Nuclear Medicine Findings
PET/CT
Generally performed when primary remains occult following CT/MR
Increases frequency of primary site detection from 25% to 50%
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree