51 Septic arthritis
Background
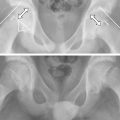
Septic arthritis refers to infection of a joint. It can occur in several different patient groups: in adults post-joint replacement, post-traumatically or spontaneously, especially in diabetics. Another important patient group is the limping child with a septic hip (see discussion in Chapter 59, ‘Perthes’ disease’).
Clinical features
Age is the key discriminator. SUFE most commonly occurs in 10–16-year-olds (see Chapter 58) and Perthes’ disease in children aged 5–12 (see Chapter 59). These patients are usually systemically well. Irritable hip occurs in children aged 3–10. There is usually a preceding or concomitant viral illness. Systemic pyrexia is unusual.
One study [1] demonstrated that paediatric patients who were non-weight-bearing, with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) > 40, white cell count >12 × 109/L and fever almost always had septic arthritis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree