Septic Arthritis (Knee)
Brett R. Murdock
Daniel B. Nissman
CLINICAL HISTORY
43-year-old female with a history of lupus treated with steroids, presents with developing left knee pain, swelling, and fevers.
FINDINGS
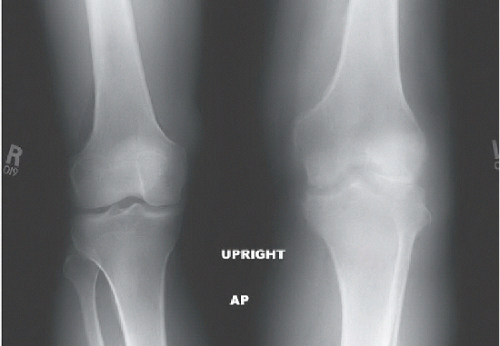
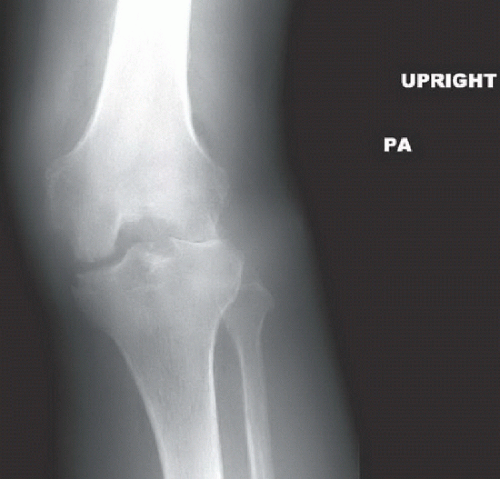
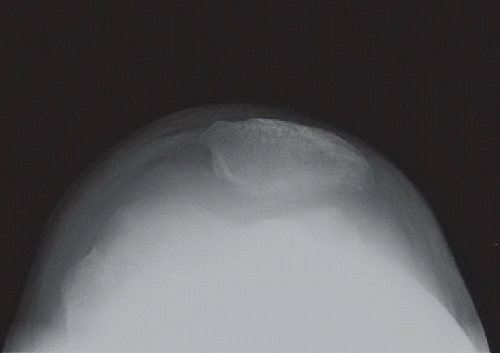
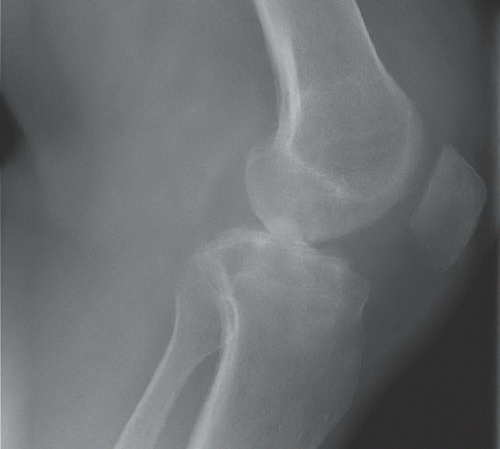
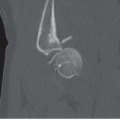
Radiographs of the left knee reveal an erosive process involving the tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joints with an associated effusion and subcutaneous soft tissue edema. Comparison to the normal knee is seen in the standing AP radiographs of both knees (Fig. 88A). The erosive disease, mostly characterized by pitting and indistinctness of the subchondral bone, is best appreciated on the flexed PA radiograph (Fig. 88B) and the tangential patellar radiograph (Fig. 88C); an overt marginal erosion is seen in the medial aspect of the medial tibial plateau. The effusion and soft tissue swelling are best appreciated on the lateral (Fig. 88D) and tangential patellar radiographs.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Rheumatoid arthritis, septic arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthropathy, or crystal deposition disease.