Sickle Cell Anemia
R. Brooke Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Hemolytic anemia due to abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in deformation of red blood cells and leading to microvascular occlusion and infarcts
Imaging
Best imaging tool
NECT to visualize calcified spleen
US to visualize gallstones
Chest and spine radiographs for pulmonary and spinal findings
Best diagnostic clue
Small, densely calcified spleen on NECT
Papillary necrosis on IVP; cholelithiasis in African-American pediatric patient
Top Differential Diagnoses
Asplenia
Splenectomy
Papillary necrosis from other causes
Bone infarcts from other causes
Clinical Issues
Most common signs/symptoms
Acute, painful vasoocclusive crisis
Acute bone and chest pain
Prognosis improving
Median survival in United States now 40-50 years
In adulthood, end organ failure has major impact on survival
Diagnostic Checklist
Consider prior splenectomy if spleen not identified
Image interpretation pearls
Constellation of chest, bone, renal, and splenic lesions supports diagnosis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Sickle cell anemia (SCA)
Definitions
Hemolytic anemia due to abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in deformation of red blood cells and leading to microvascular occlusion and infarcts
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
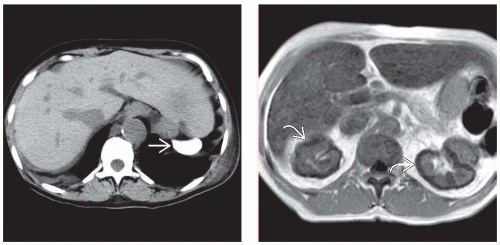
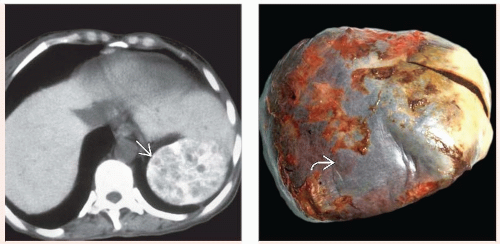
Small, densely calcified spleen on NECT
Papillary necrosis on IVP
Cholelithiasis in African-American pediatric patient
Salmonella osteomyelitis in young African-American patient
Size
Spleen may be undetectable (autosplenectomy) but rarely may enlarge due to sequestration syndrome
Imaging Recommendations
Best imaging tool
NECT to visualize calcified spleen
US to visualize gallstones
Chest and spine radiographs for pulmonary and spinal findings
Radiographic Findings
Radiography
Chest x-ray
Bacterial pneumonia, pleural effusion
Enlarged heart due to anemia
Pulmonary opacities due to pulmonary infarcts and hemorrhage
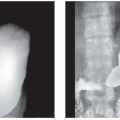
H-shaped vertebrae in spine
Paraspinous extramedullary hematopoiesis
Abdominal radiograph
Small, calcified spleen
Splenomegaly due to sequestration syndrome
Skull radiograph
Marrow expansion with thickened, striated appearance
Long bone radiographs
Patchy sclerosis and radiolucency due to infarcts
Osteonecrosis
Areas of osteomyelitis (Salmonella)

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree