Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma
Michelle A. Michel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC)
Rare, aggressive, sinonasal nonsquamous cell epithelial or nonepithelial malignant neoplasm of varying histogenesis
Imaging
Aggressive sinonasal mass with bone destruction & rapid growth
Large, typically > 4 cm at presentation
Origin most common in nasal cavity with extension into paranasal sinuses; ethmoid origin more common than maxillary
Bone CT: Poorly defined, soft tissue SN mass with aggressive bone destruction
MR: Isointense to muscle on T1
Low to intermediate T2 signal
Heterogeneous enhancement with necrosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
Sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma
Esthesioneuroblastoma
Sinonasal non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Sinonasal adenocarcinoma
Clinical Issues
Higher propensity for distant metastases to bone, brain & dura, liver, & cervical nodes than other sinonasal malignancies
Diagnostic Checklist
Imaging features are nonspecific
Tumor growth rate & presence of nodes/distant metastases helpful for suggesting SNUC
Consider extending coverage to evaluate for intracranial (particularly dural) & cervical nodal disease
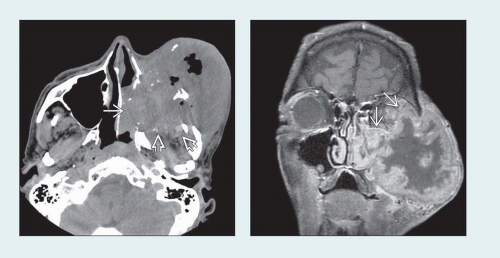 (Left) Axial NECT demonstrates a large mass in the left maxillary antrum with marked bone destruction and extension into the nasal cavity
 , masticator space , masticator space 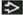 , and soft tissues of the cheek. Foci of air are seen within the necrotic portion of this rapidly growing lesion. (Right) Coronal T1WI C+ FS MR in the same patient shows a thick, nodular enhancing rim at the periphery of the mass with central necrosis. There is aggressive invasion of the orbit , and soft tissues of the cheek. Foci of air are seen within the necrotic portion of this rapidly growing lesion. (Right) Coronal T1WI C+ FS MR in the same patient shows a thick, nodular enhancing rim at the periphery of the mass with central necrosis. There is aggressive invasion of the orbit  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|