KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Microbial infection of subcutaneous tissue (cellulitis), muscle (myositis), tendon (tenosynovitis), or fascia (fasciitis)
- •
Abscess is focal fluid collection containing suppurative inflammatory material
Imaging
- •
Cellulitis
- ○
Edematous, hyperechoic, hyperemic subcutaneous fat with thickened interlobular septa
- ○
- •
Infectious tenosynovitis
- ○
Synovial tendon sheath is thickened, hyperemic, and contains fluid surrounding tendon
- ○
- •
Infectious myositis
- ○
Hyperechoic, hyperemic, and indistinct, ± abscess
- ○
- •
Necrotizing fasciitis
- ○
Spreads rapidly between tissue planes
- ○
Thickened, irregular fascia with perifascial fluid
- ○
Gas is highly specific but not always present
- ○
- •
Abscess
- ○
Variable echogenicity, peripheral hyperemia, ± septation/gas
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
Route of spread can be direct (skin), postsurgical, or hematogenous
- •
Deep soft tissue infection may require hospitalization, IV antibiotics, &/or surgery
- •
Necrotizing fascitis is life threatening and early diagnosis decreases morbidity
Scanning Tips
- •
Use wide field of view and increase depth to ensure entire area of abnormal tissue is imaged
- •
Diagnose abscess by demonstrating fluctuance and lack of color Doppler flow
- •
Note and report visible skin changes, breeches, or crepitus
- •
Assess nearby joints for effusion (septic arthritis) and adjacent bone for cortical irregularity (osteomyelitis)
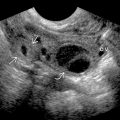
 with intervening hyperechoic fat lobules
with intervening hyperechoic fat lobules  .
.
 shows marked expansion of the tendon sheath
shows marked expansion of the tendon sheath  with complex fluid
with complex fluid  as well as marked subcutaneous edema and hyperemia.
as well as marked subcutaneous edema and hyperemia.
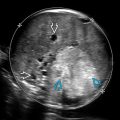
 with an intramuscular abscess
with an intramuscular abscess  containing layering debris.
containing layering debris.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree