KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Epithelial tumor of exocrine pancreas with low-grade malignant potential and solid and cystic features
Imaging
- •
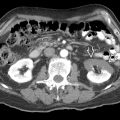
Usually large (average: 10 cm; range: 2.5-20.0 cm)
- •
Commonly in pancreatic tail
- •
Lesions < 3 cm with solid, homogeneous appearance
- •
Larger lesions: Heterogeneous mass with solid and central cystic components (hemorrhage and necrosis), fluid debris level
- •
May contain dystrophic calcifications
- •
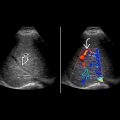
Color Doppler: Hypovascular, due to areas of necrosis
- •
Endoscopic ultrasound: More sensitive for small mass; can guide fine-needle aspiration biopsy
- •
Best imaging tool: CT and MR for demonstrating intratumoral hemorrhage and enhancing capsule/solid components
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Mucinous cystic pancreatic tumor
- •
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor
- •
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma
- •
Pancreatic ductal carcinoma
Pathology
- •
Fibrous, hypervascular capsule with solid and pseudopapillary tissue surrounding hemorrhagic and necrotic center
Clinical Issues
- •
Very rare, < 3% of all pancreatic tumors
- •
Typically in asymptomatic, young, non-Caucasian women
- ○
Termed “daughter lesion”
- ○
- •
~ 90% female; < 35 years of age
- •
Usually asymptomatic or nonspecific abdominal pain
- •
May have palpable abdominal mass
- •
Usually benign but with low malignant potential
- ○
< 10% metastasize or recur
- ○
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Consider diagnosis if encapsulated pancreatic tail mass with solid, cystic, and hemorrhagic components is found in young non-Caucasian female and there is no pancreatic ductal dilation
Scanning Tips
- •
Look for solid components, which will triage patient to surgery
 and cystic or hemorrhagic
and cystic or hemorrhagic  components.
components.
 arising from the body of pancreas. The center
arising from the body of pancreas. The center  was more cystic. The neck of the pancreas
was more cystic. The neck of the pancreas  was normal.
was normal.
 in the solid component of the solid pseudopapillary neoplasm. The splenic vein
in the solid component of the solid pseudopapillary neoplasm. The splenic vein  was patent.
was patent.