| SKULL BASE REGION | Suprasellar |
| HISTOPATHOLOGY | Meningioma, WHO grade I |
| PRIOR SURGICAL RESECTION | Yes |
| PERTINENT LABORATORY FINDINGS | Prolactin: 60 ng/mL |
Case description
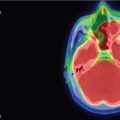
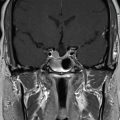
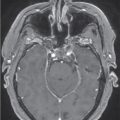
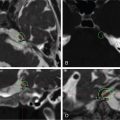
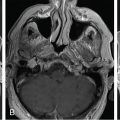
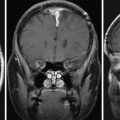
The patient is a 49-year-old female who presented with nipple discharge, no neurological deficit, and a mildly elevated prolactin level at 60 ng/mL (normal range 2–29 ng/mL). Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a homogenously enhancing suprasellar mass causing pituitary stalk deviation with contiguous extension to the left cavernous sinus ( Figure 4.18.1 ). Hormone replacement with hydrocortisone of 20 mg in the morning and 10 mg in the evening was initiated for 2 weeks prior to surgery. The approach was a surgical debulking via neuronavigated endonasal endoscopy. Postoperative recovery was uneventful, and histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of a meningioma WHO grade I. Residual tumor, which was mostly inside the left cavernous sinus ( Figure 4.18.2 ), was then treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) 3 months after surgery ( Figure 4.18.3 ).
| Radiosurgery Machine | CyberKnife |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) | 27.5, at the 80% isodose line |
| Number of Fractions | 5 |



| Critical Structure | Dose Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Optic nerve/chiasm | 25 max per 5 fractions / <0.2cc>20 Gy |
| Brainstem |
|
| Cranial nerves in cavernous sinus |
|
| Cavernous carotid artery |
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree