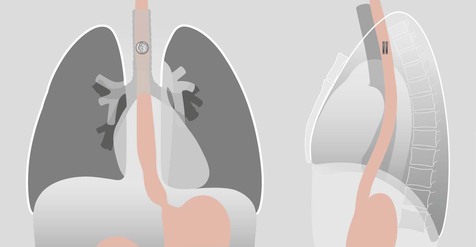
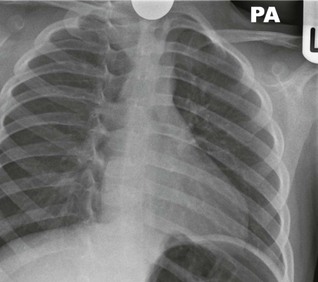
Occasionally, a coin will lodge in the oesophagus. Some of these patients will be asymptomatic. An unrecognised coin can cause clinical problems including erosion of the mucosa which may result in an abscess or mediastinitis4. It is important to confirm that any swallowed coin has passed beyond the oesophagus. If the CXR is clear then the parents can be reassured that the coin will be passed within a few days. Does the stool need to be checked? Sometimes a coin will be overlooked in the stool; the parents would be better advised to return to the Emergency Department (ED) only if the child becomes symptomatic. Coin composition: coins in the UK and in the European Union are made of steel or alloys of various metals and sometimes coated with copper. In effect, these coins are inert. This does not apply worldwide. For example, in 1982 because of the cost of copper the one cent coin in the USA (commonly referred to as the penny) was minted with a mainly zinc core and a thin copper coating. Interaction between gastric acid and zinc can cause ulceration in the stomach. This possibility led to various scares and the consequent overuse of routine AXR. The penny constituents were not changed, but eventually a practical recommendation was made and widely adopted: if a USA penny has been swallowed and the CXR is clear then an AXR need only be obtained in a child who subsequently developes intestinal symptoms. The latter is an exceptionally rare occurrence.
Swallowed foreign bodies
The most common foreign bodies1
Children: coins
Radiography…
Swallowed foreign bodies
21