9 The Skull
SKULL BASELINES
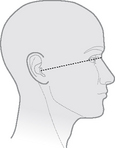
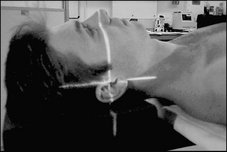
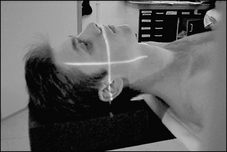
Orbitomeatal baseline
Line joins the outer canthus of the eye to the midpoint of the external auditory meatus
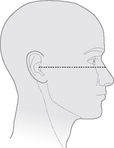
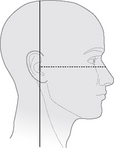
Anthropological baseline
Line joins the infraorbital margin to the superior border of the external auditory meatus.
The difference in angles between the orbitomeatal baseline and the anthropological baseline is 10°
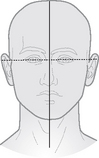
Interpupillary line
Line joins the centre of the two orbits and is perpendicular to the median sagittal plane
Notes:__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
ISOCENTRIC TECHNIQUE
![]() Total immobilisation of the patient is essential
Total immobilisation of the patient is essential
![]() Patient can be examined erect or supine – easier to immobilise when supine
Patient can be examined erect or supine – easier to immobilise when supine
![]() Overexposure can be tolerated more than underexposure
Overexposure can be tolerated more than underexposure
![]() Dulac technique is positioning patient so that the area of interest is in the centre of a sphere – isocentre
Dulac technique is positioning patient so that the area of interest is in the centre of a sphere – isocentre
![]() Unsure of your position – move the tube 180° to check the other side
Unsure of your position – move the tube 180° to check the other side
![]() Up to 50% reduction in dose can be achieved
Up to 50% reduction in dose can be achieved
![]() Radiation protection – use cones and collimators to limit the beam – most important – to avoid the need for repeats
Radiation protection – use cones and collimators to limit the beam – most important – to avoid the need for repeats
![]() Some radiographs may appear different – due to decrease in distortion and true representation of the patient
Some radiographs may appear different – due to decrease in distortion and true representation of the patient
![]() Skull #s – linear is most common – stellate is star shaped.
Skull #s – linear is most common – stellate is star shaped.
![]() Depressed – detached fragment and may be comminuted
Depressed – detached fragment and may be comminuted
![]() Where possible the patient should remain in a comfortable position – different projections achieved by moving the tube
Where possible the patient should remain in a comfortable position – different projections achieved by moving the tube
Tube column
• Tube and vertical arm is set to 0° so that it is perpendicular to the table top
• Sagittal light beam should coincide with median sagittal plane and the transverse light beam with the anthropological plane
• Horizontal beam must pass through auditory canals and coincide with auricular plane
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree